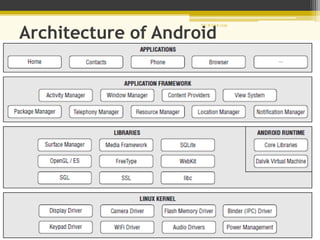
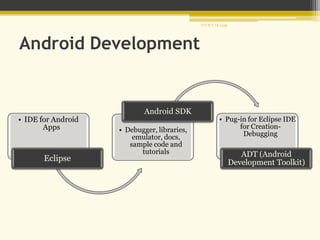
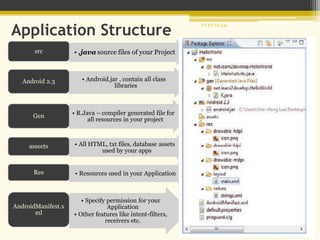
Android is an open-source software platform and operating system for mobile devices based on the Linux kernel. It allows developers to write managed code in Java and offers a unified approach to application development so an app can run on numerous devices. The architecture of Android includes four main layers - the Linux kernel, libraries, Android runtime, and applications framework.