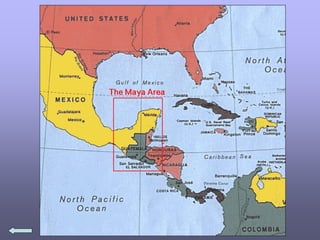
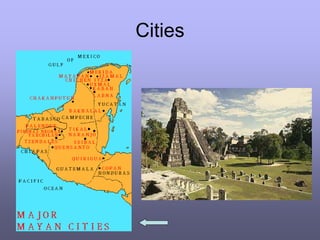
The ancient Mayans developed an advanced civilization in Mexico and Central America around 2600 BC. They were accomplished mathematicians, astronomers, and invented a sophisticated form of writing. Mayan cities centered around ceremonial pyramids and were important religious and political centers governed by priests. The Mayans had an advanced understanding of astronomy, mathematics, and developed accurate calendars. They also practiced human sacrifice as part of their polytheistic religion, believing it would please the gods and ensure good harvests.