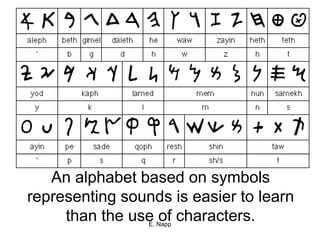
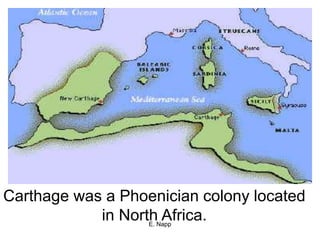
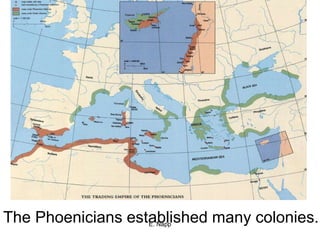
The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people who settled in city-states along the coast of present-day Lebanon. They lacked natural resources so relied on seafaring trade, coming to dominate Mediterranean trade by 900 BC. They established colonies throughout the region and invented the first alphabet, which was adopted by the Greeks and forms the basis of modern alphabets. Their trade and colonies encouraged cultural diffusion in the ancient world.