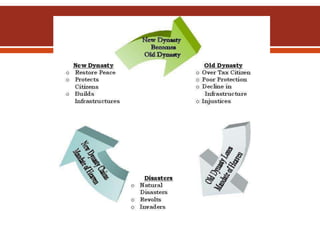
The document summarizes the geography and early history of China. It notes that China's civilization developed in isolation due to barriers like deserts and mountains. Cities grew up along two major river systems, and an isolated culture emerged with few outside influences. Over time, influential philosophies like Confucianism, Legalism, and Daoism shaped Chinese society and government. The Han Dynasty unified much of China and saw advances in technology and the opening of the Silk Road, connecting China to global trade.