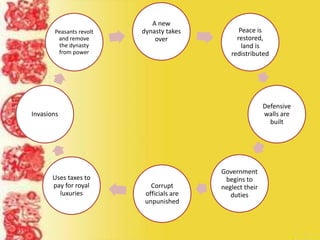
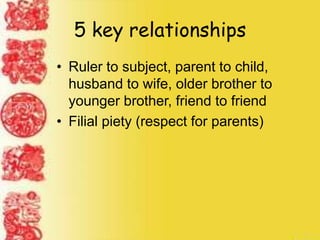
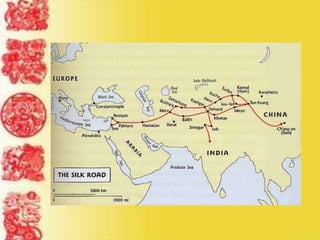
Ancient China was geographically isolated by deserts, mountains, and oceans. Civilization emerged along the Huang River valley. The Shang Dynasty, around 1766 BC, was China's first recorded dynasty and established social classes led by kings. Dynasties would rise and fall in a cyclical pattern, losing the "Mandate of Heaven" when disasters occurred. Confucius established a philosophy emphasizing relationships and filial piety that still influences a third of the world. The Qin unified China under the first emperor Shi Huangdi, who built the Great Wall and established a centralized government, while the Han Dynasty expanded the empire through expansionism and established the Silk Road for international trade.