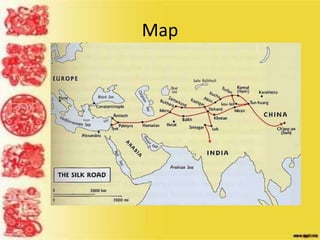
Ancient China was isolated by geographic barriers like deserts and mountains. Civilization emerged in the Huang River valley. The Shang Dynasty was the first recorded Chinese dynasty around 1766 BC and developed social classes led by kings. Dynasties would rise and fall in a cyclical pattern, needing a "Mandate of Heaven" to rule. Confucius was an influential teacher who emphasized relationships and filial piety. Achievements included silk production, books, writing, and bronze technology. The Qin unified China militarily but ruled brutally before the Han strengthened the economy through expansion and trade along the Silk Road.