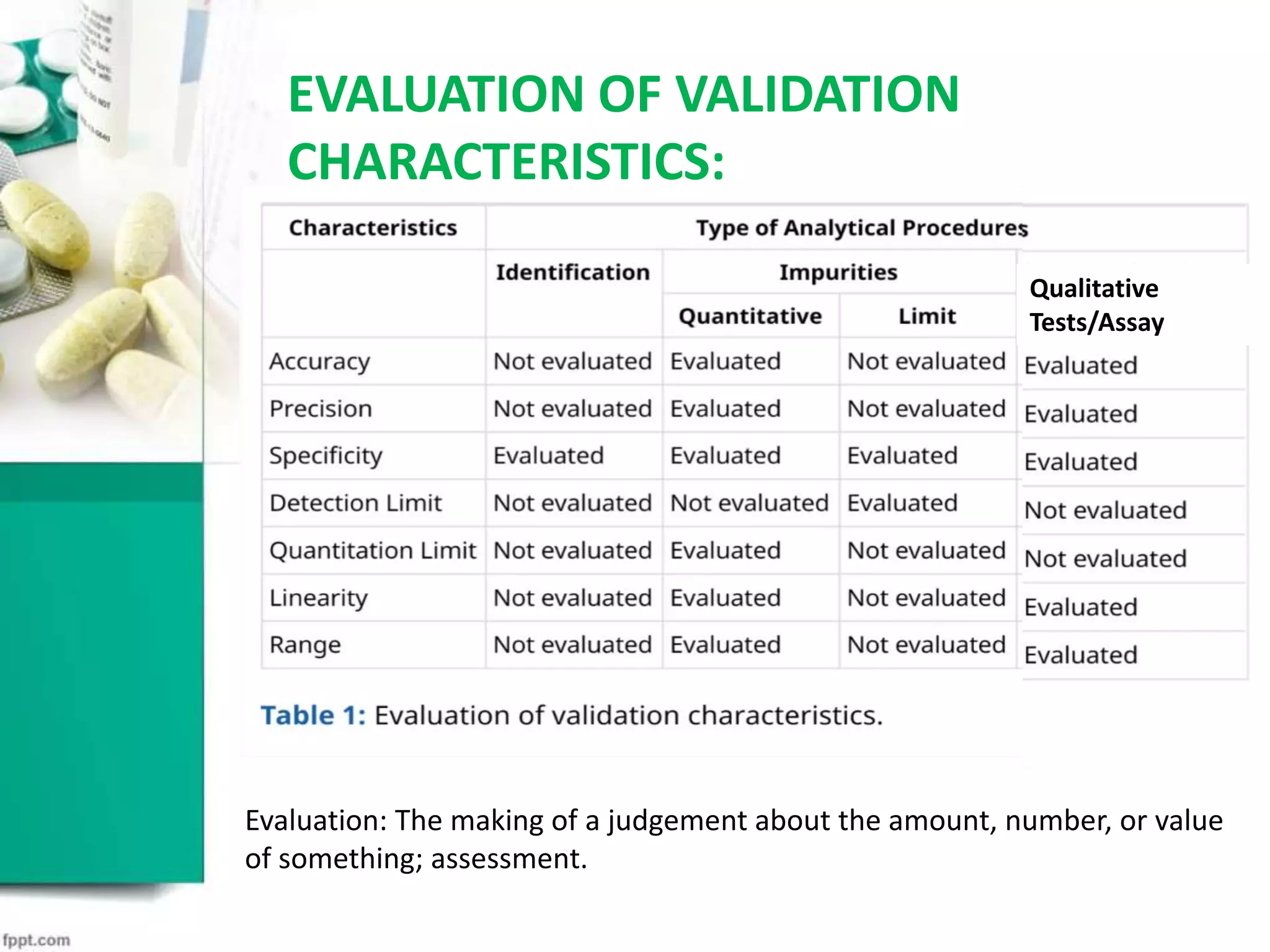
This document discusses validation in the pharmaceutical industry. It begins by defining validation as establishing evidence that a process maintains compliance. It then discusses why validation is important, including that regulatory agencies require validation to ensure consistent, reproducible results. It outlines the types of validation including equipment, facilities, analytical methods, and more. It focuses on analytical method validation, discussing parameters like accuracy, precision, specificity, and more. It emphasizes that validation is necessary to confirm analytical procedures consistently produce the intended results.