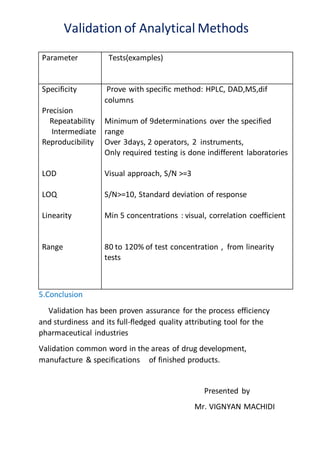
Validation of analytical methods involves establishing documented evidence that a process will consistently produce results meeting predetermined specifications. It is necessary to ensure customer satisfaction, comply with regulations, and control costs. Proper documentation of validation activities includes validation master plans, protocols, and reports. Types of validation include process, cleaning, equipment, and validation of analytical methods itself. Method validation parameters that must be checked include selectivity, precision, accuracy, linearity, range, limit of detection, limit of quantification, and robustness. Validation ensures process efficiency and quality for the pharmaceutical industry.