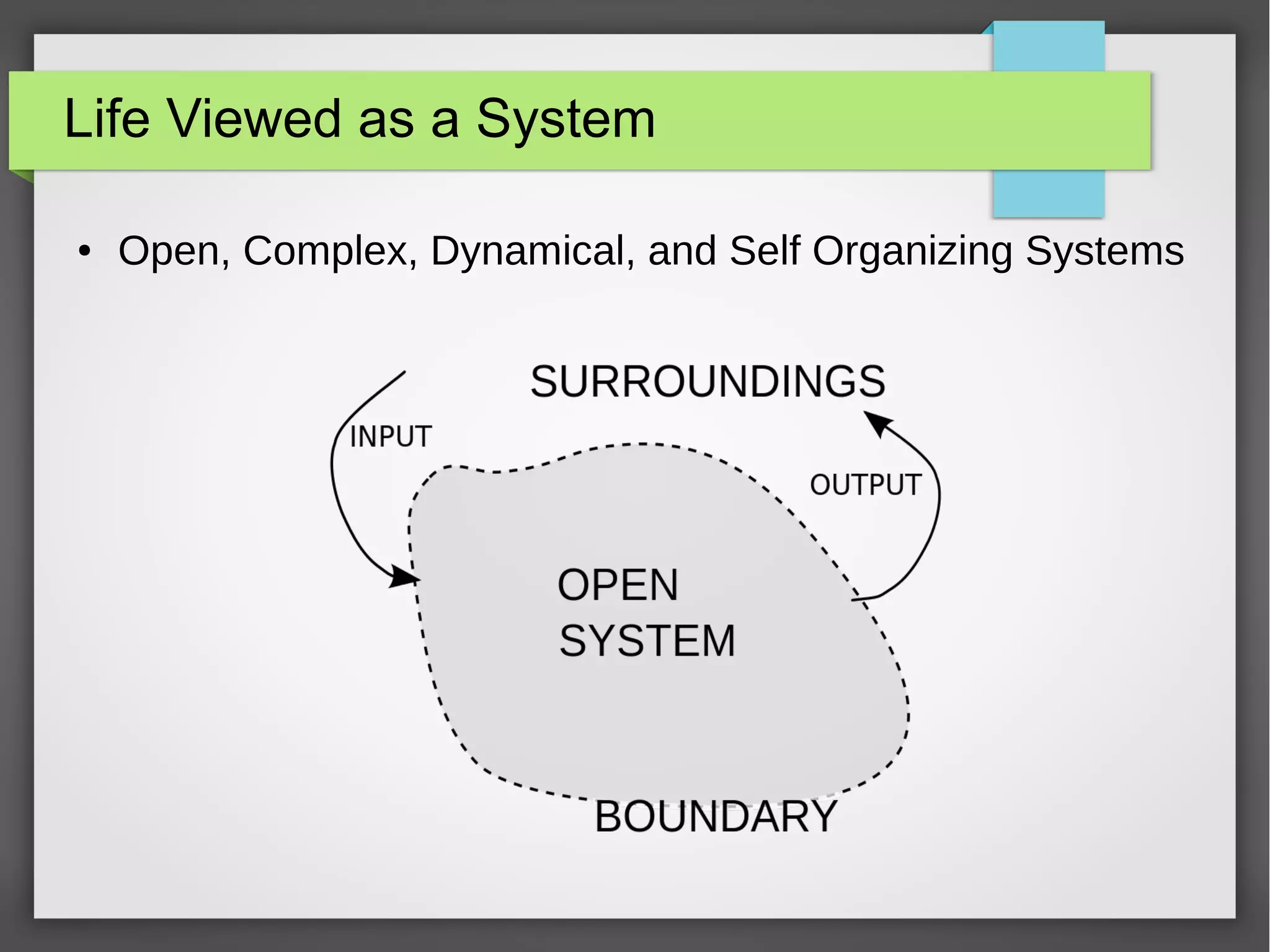
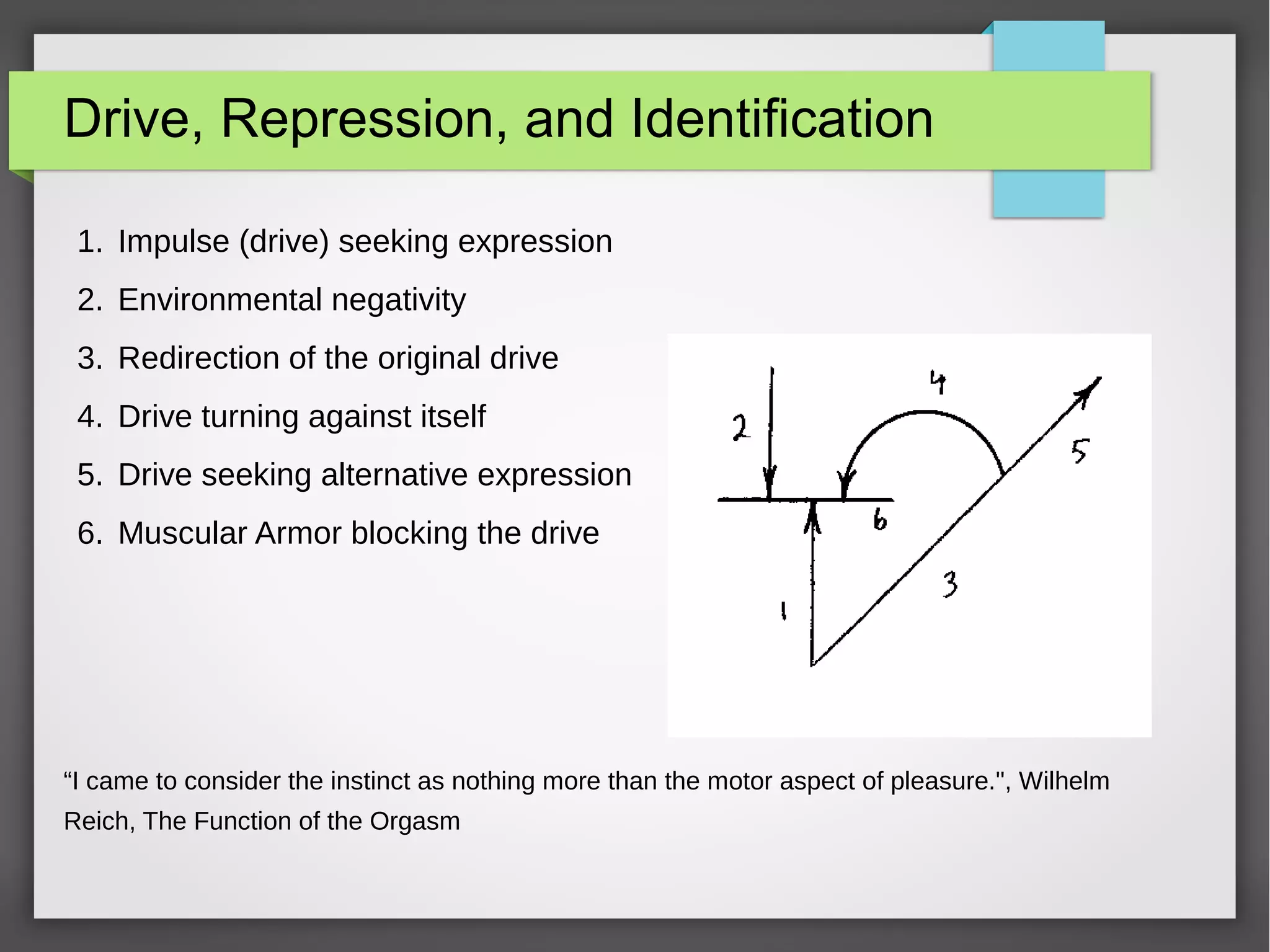
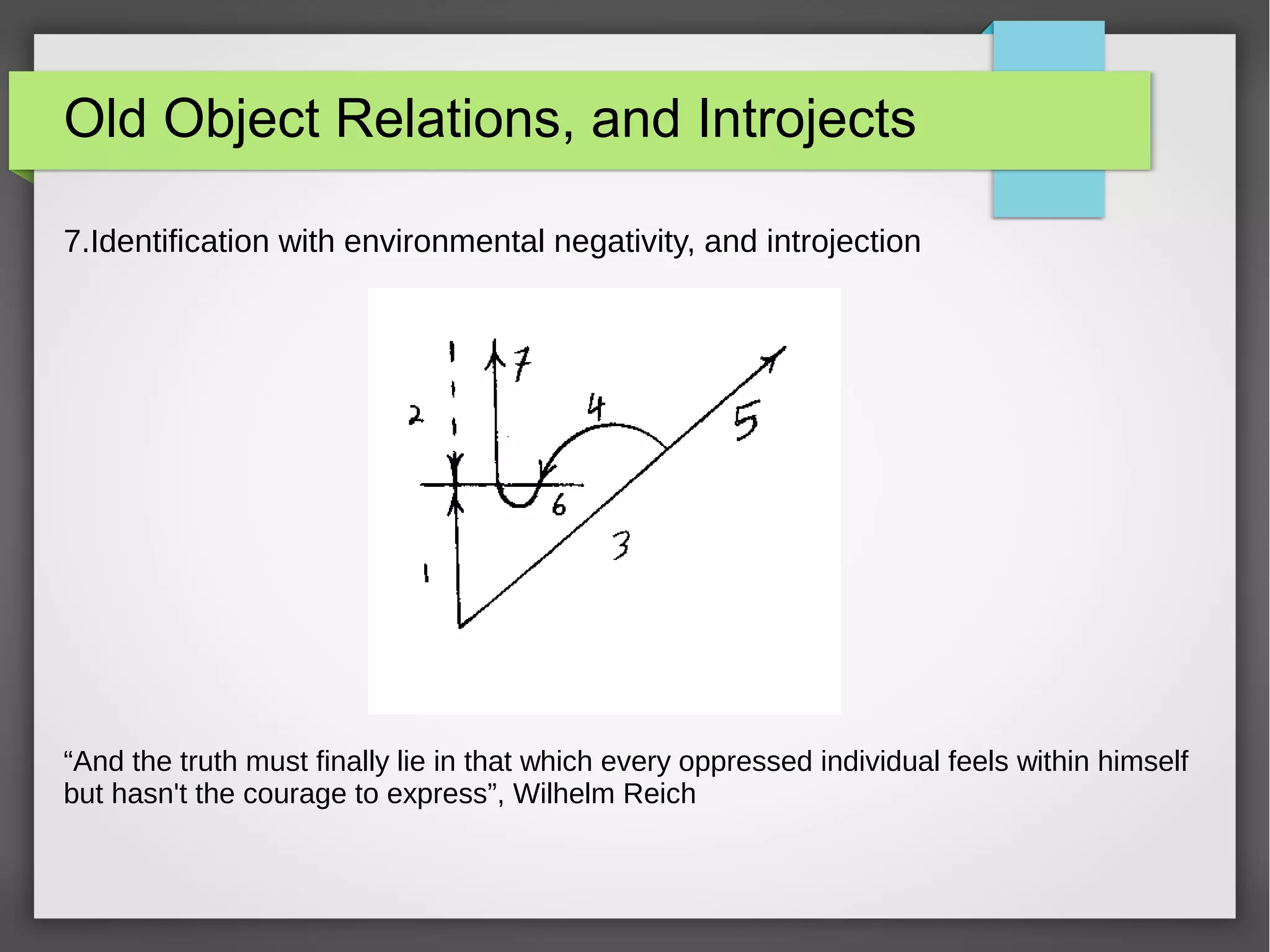
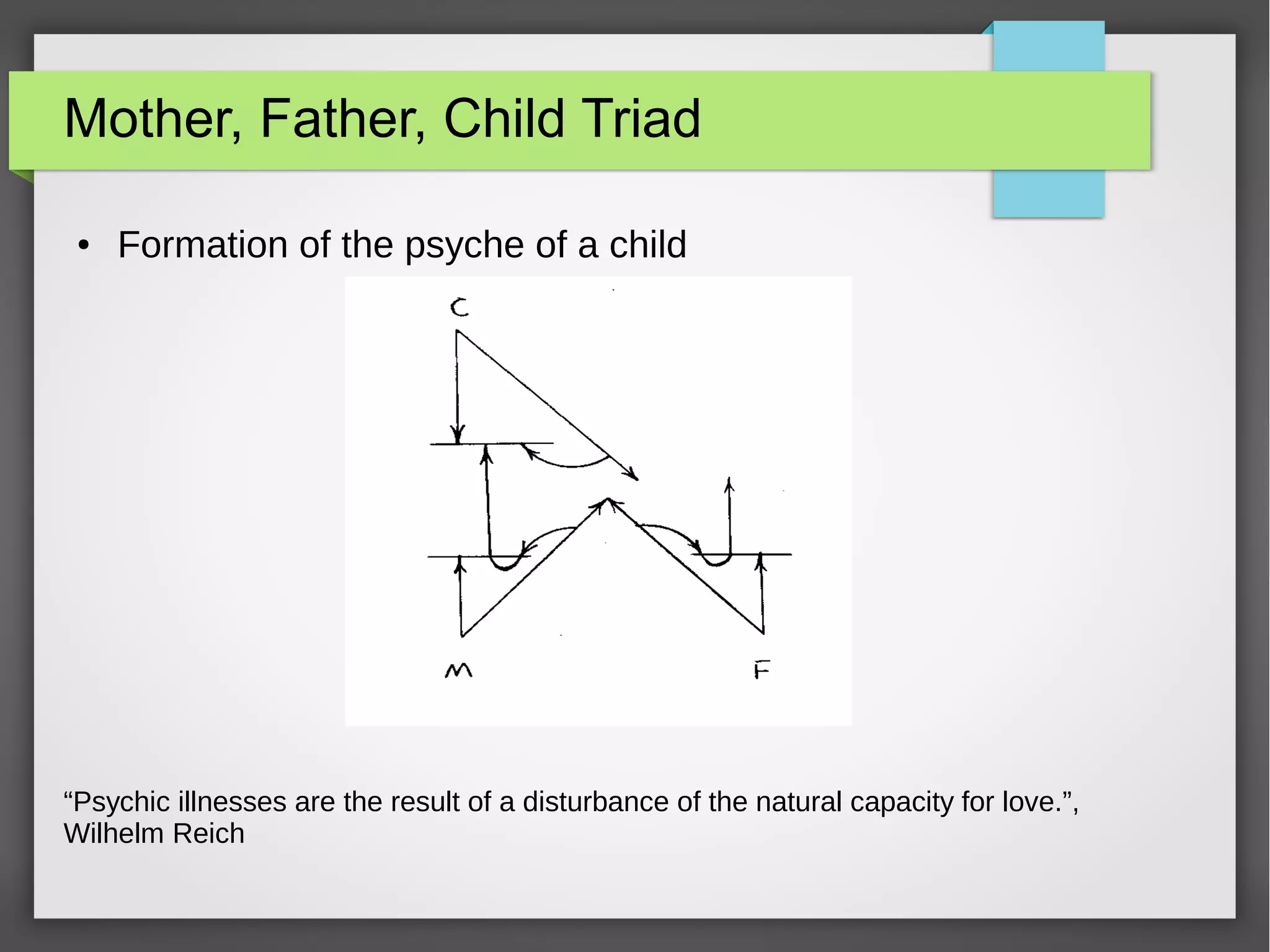
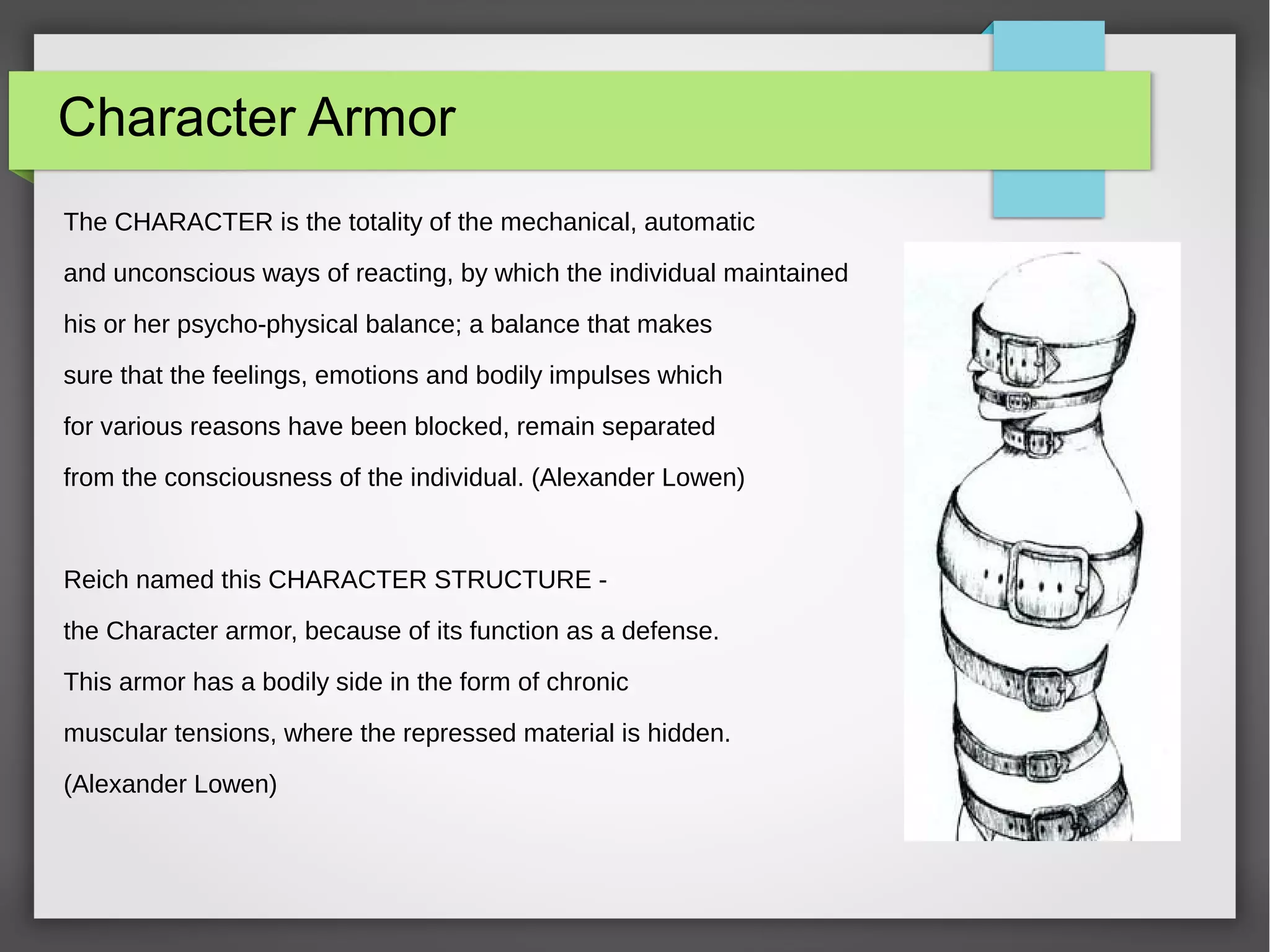
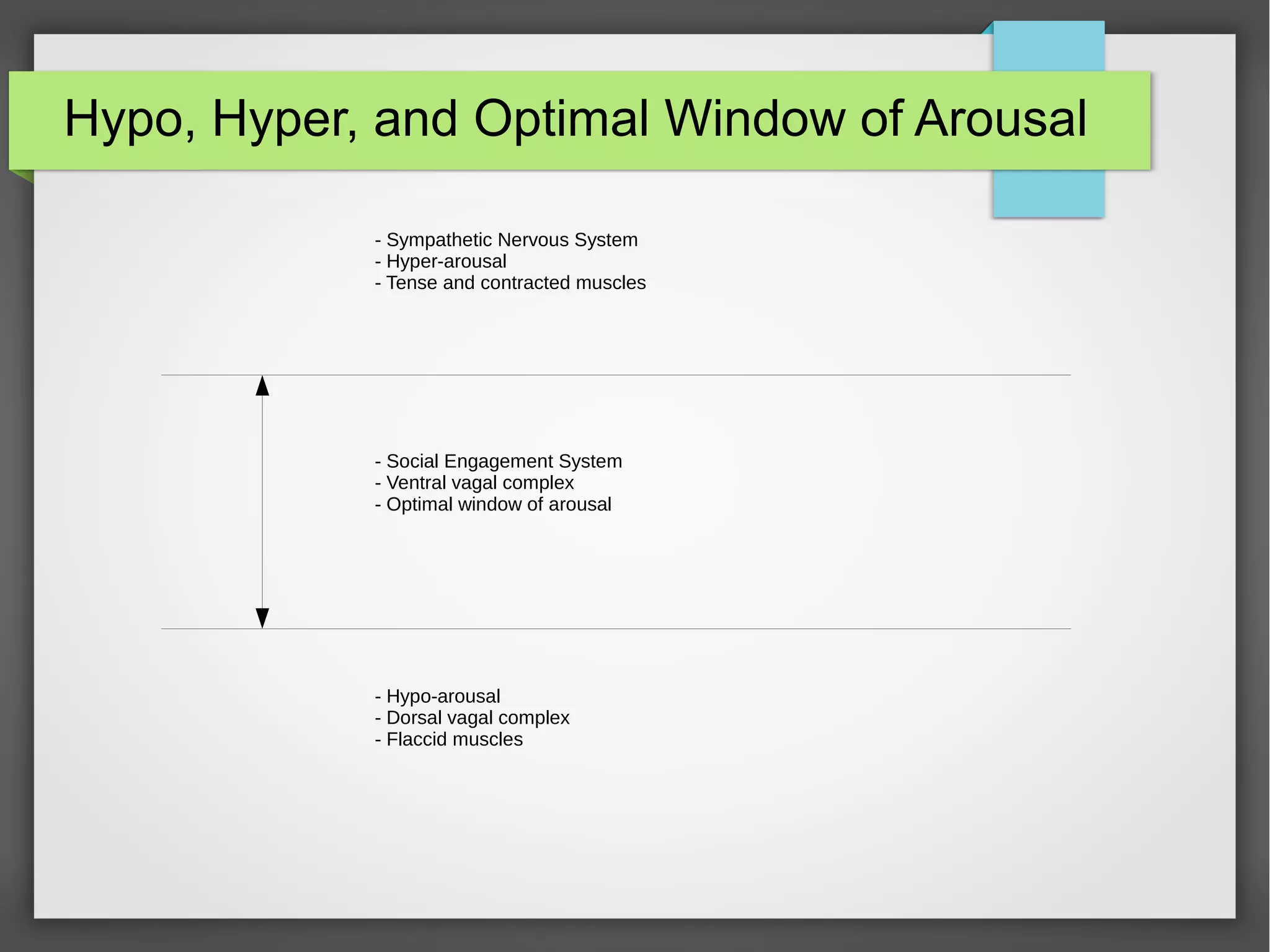
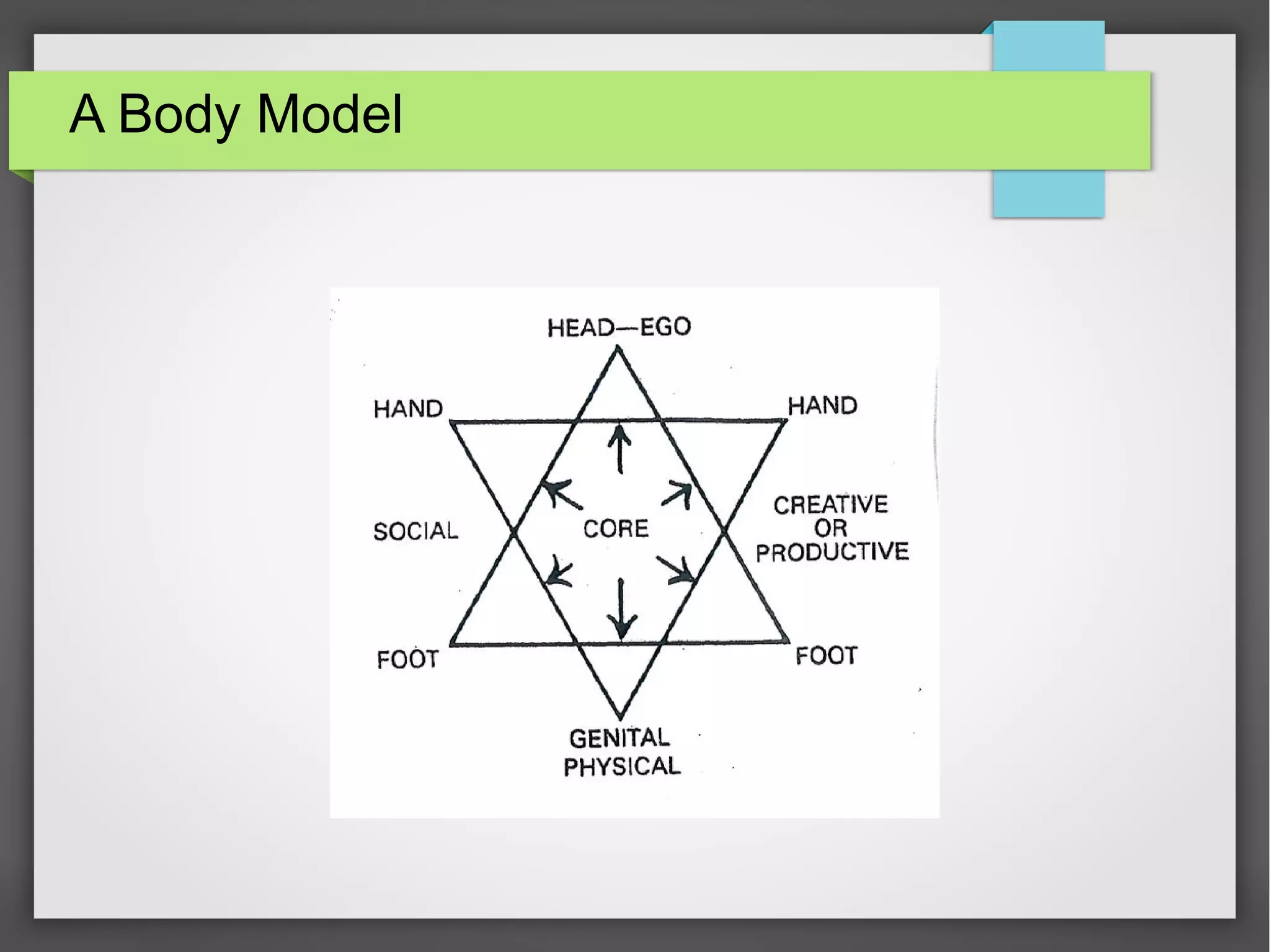
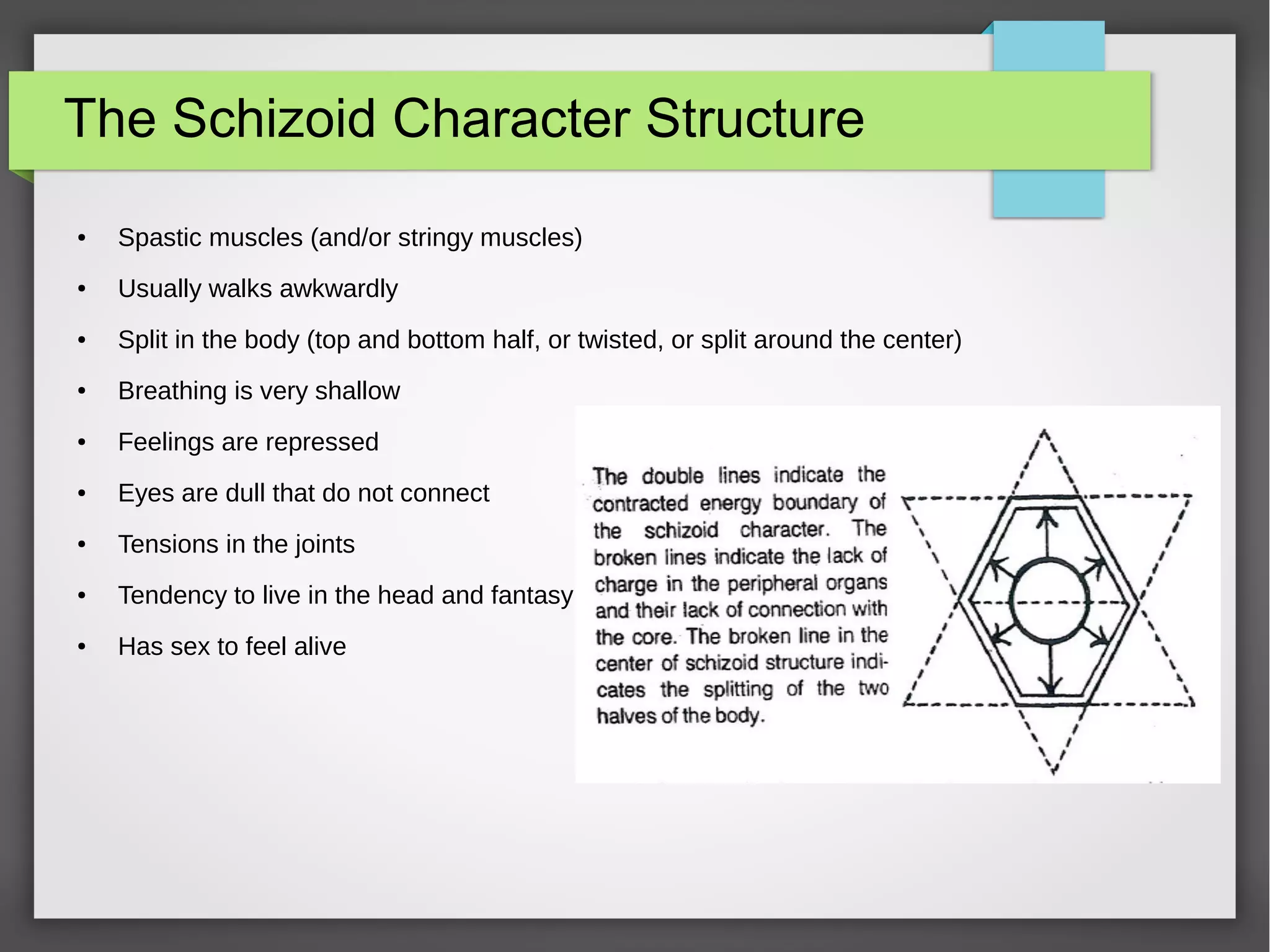
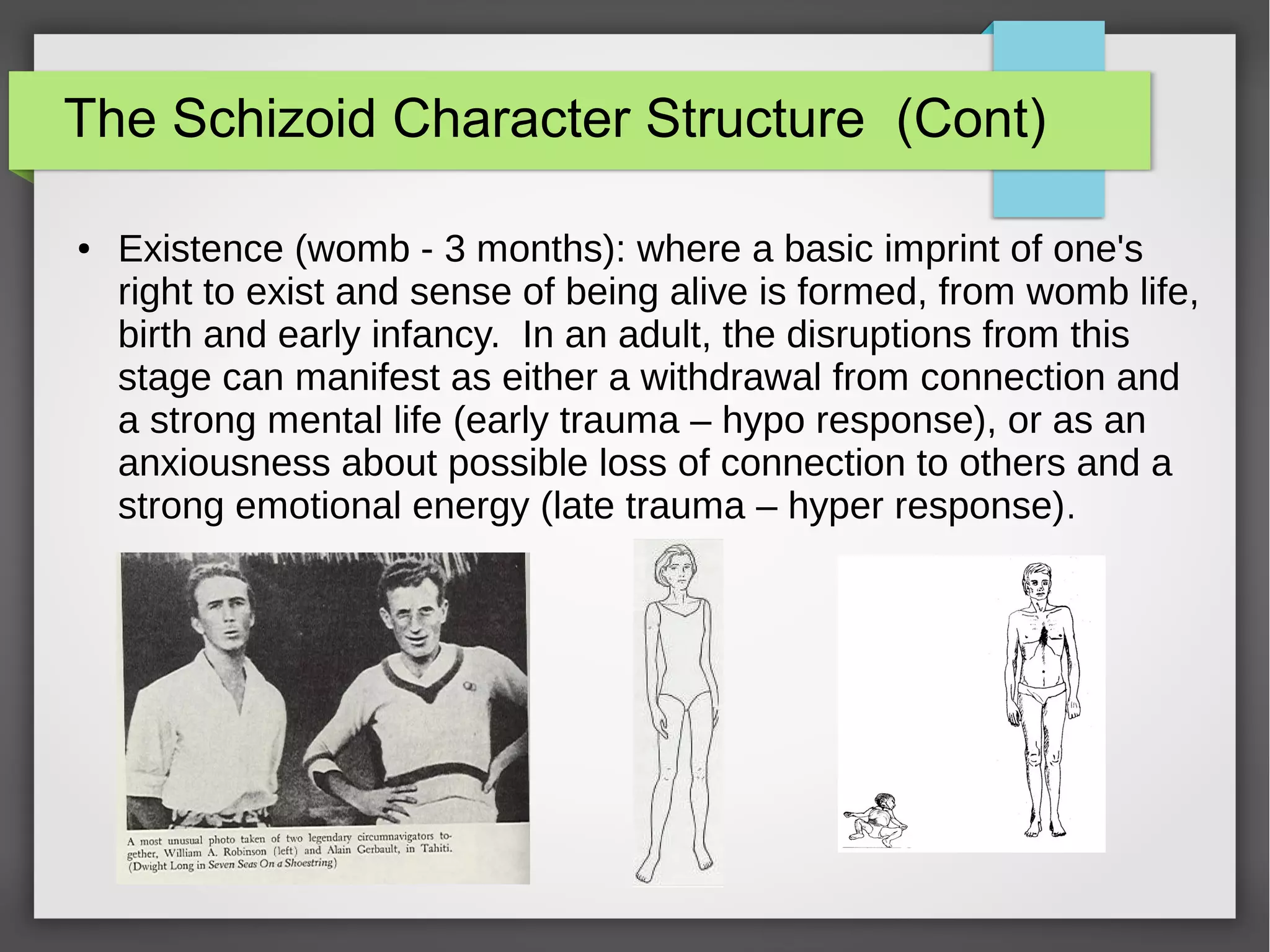
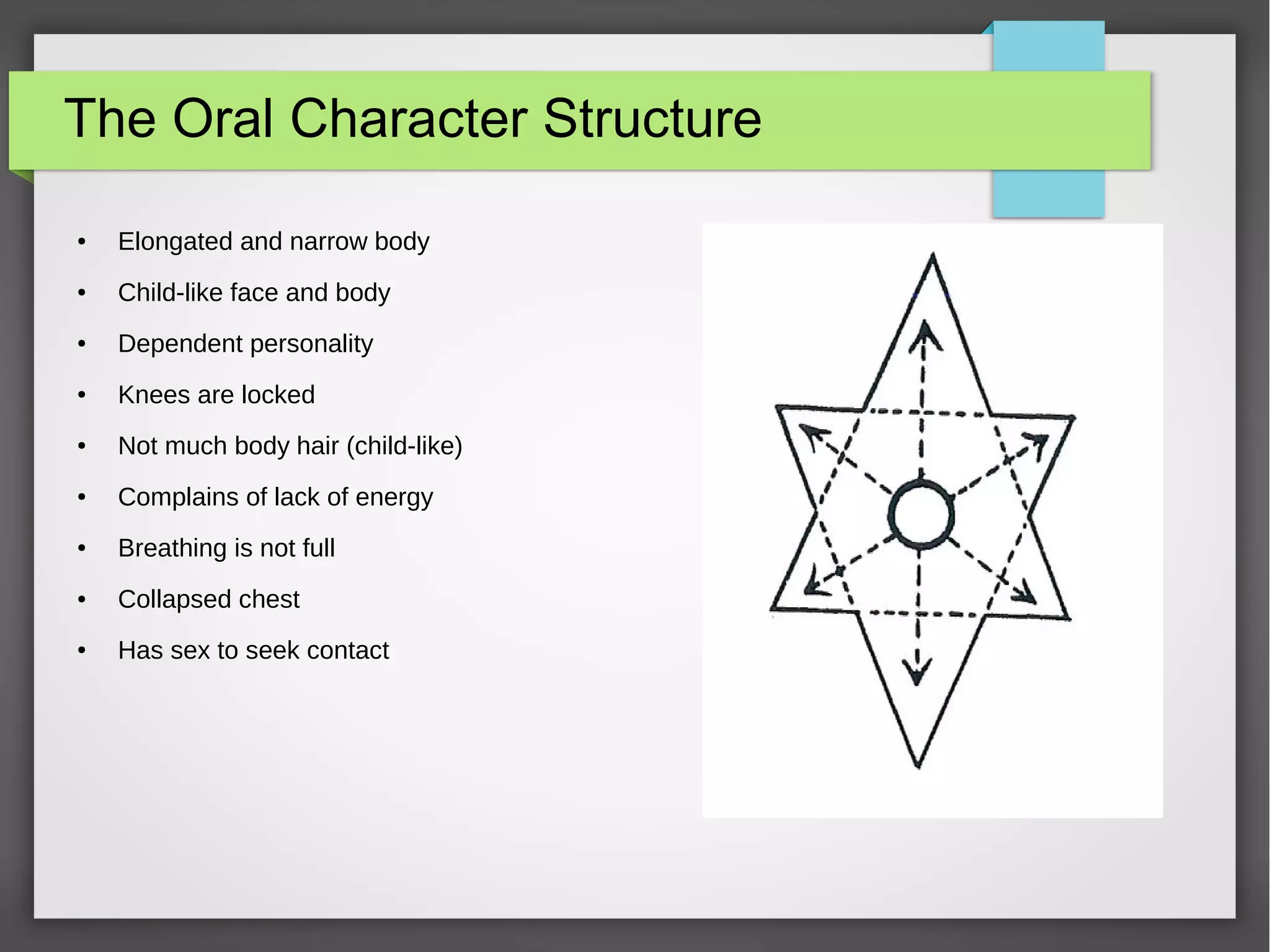
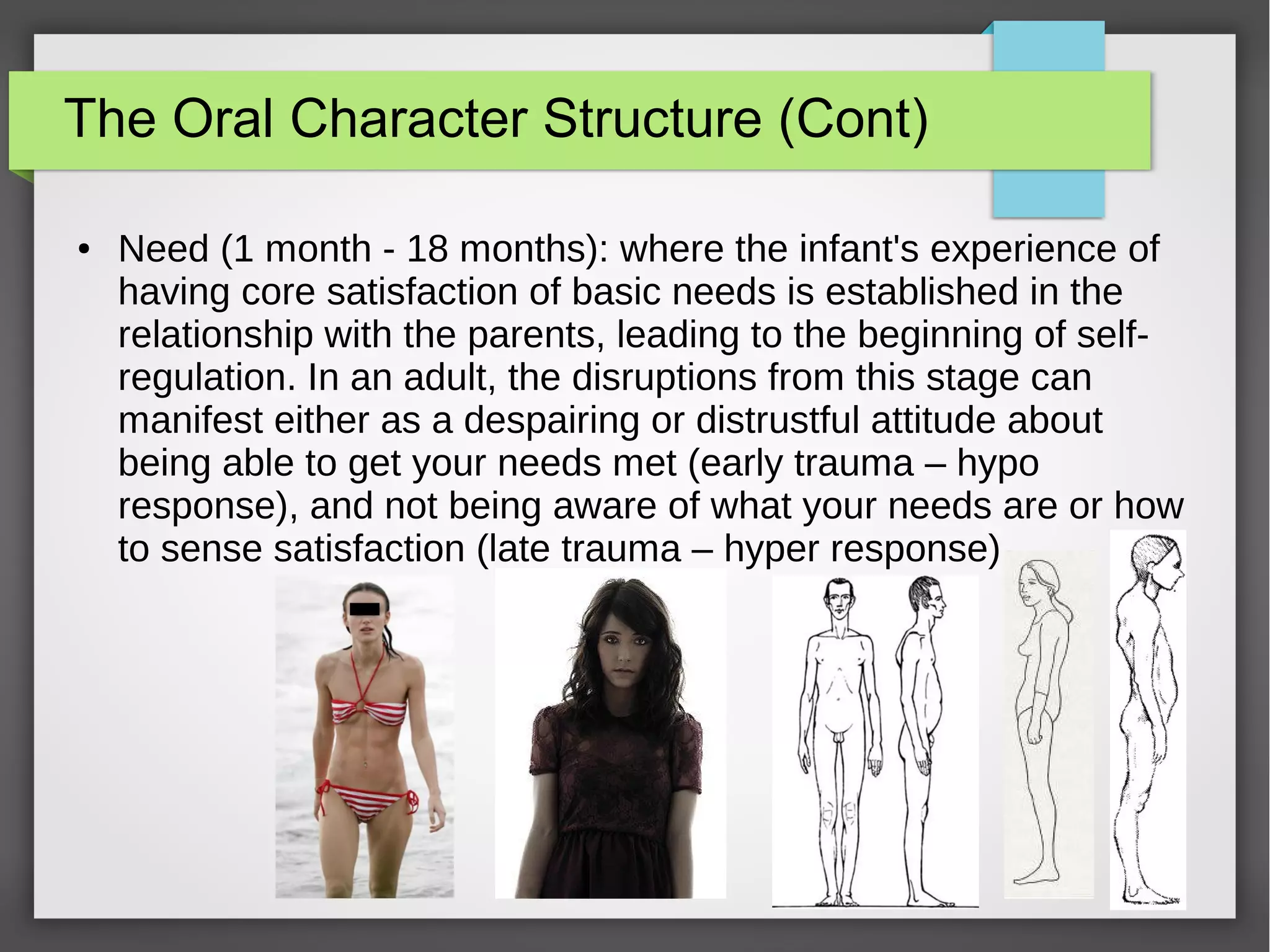
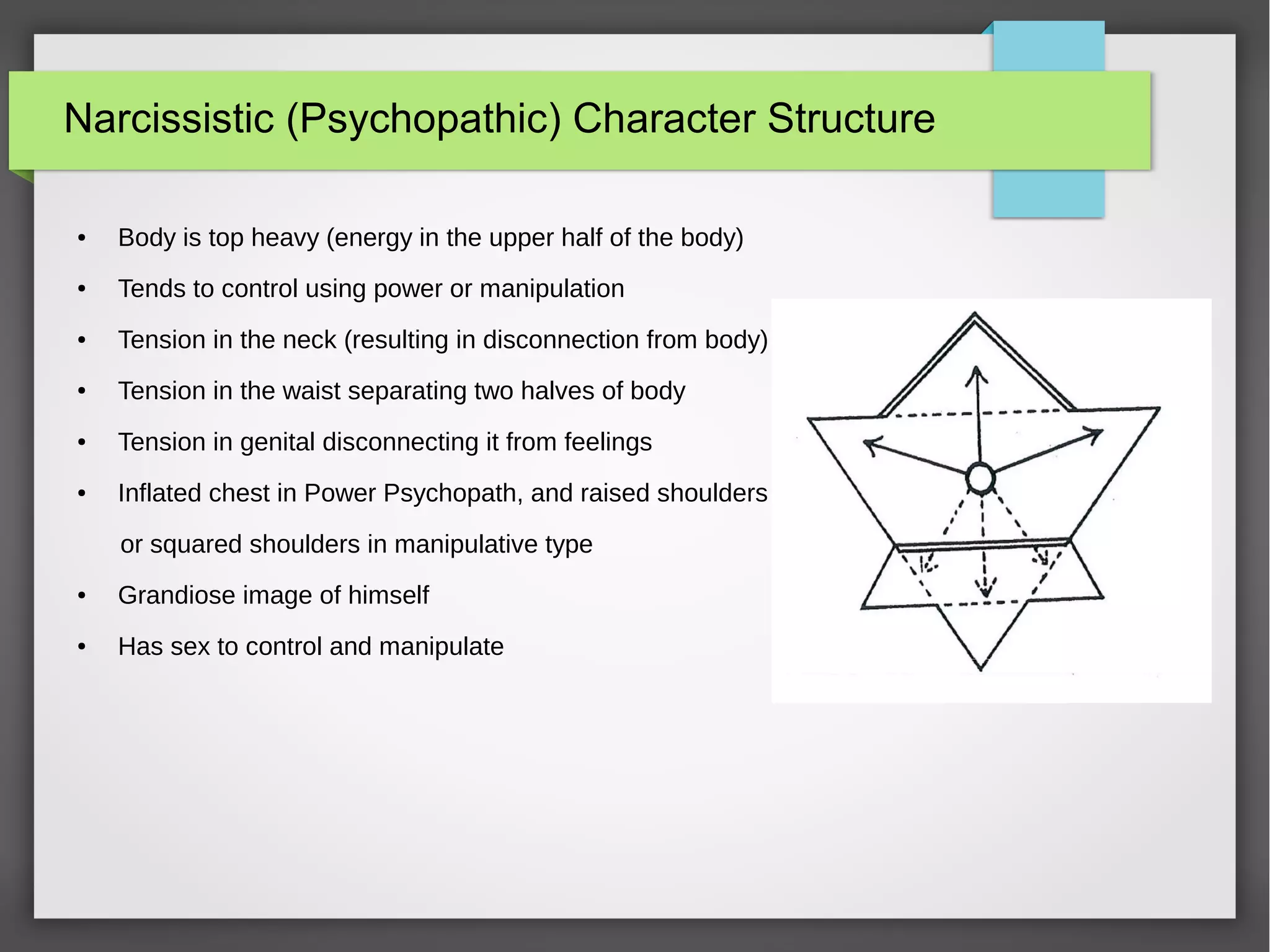
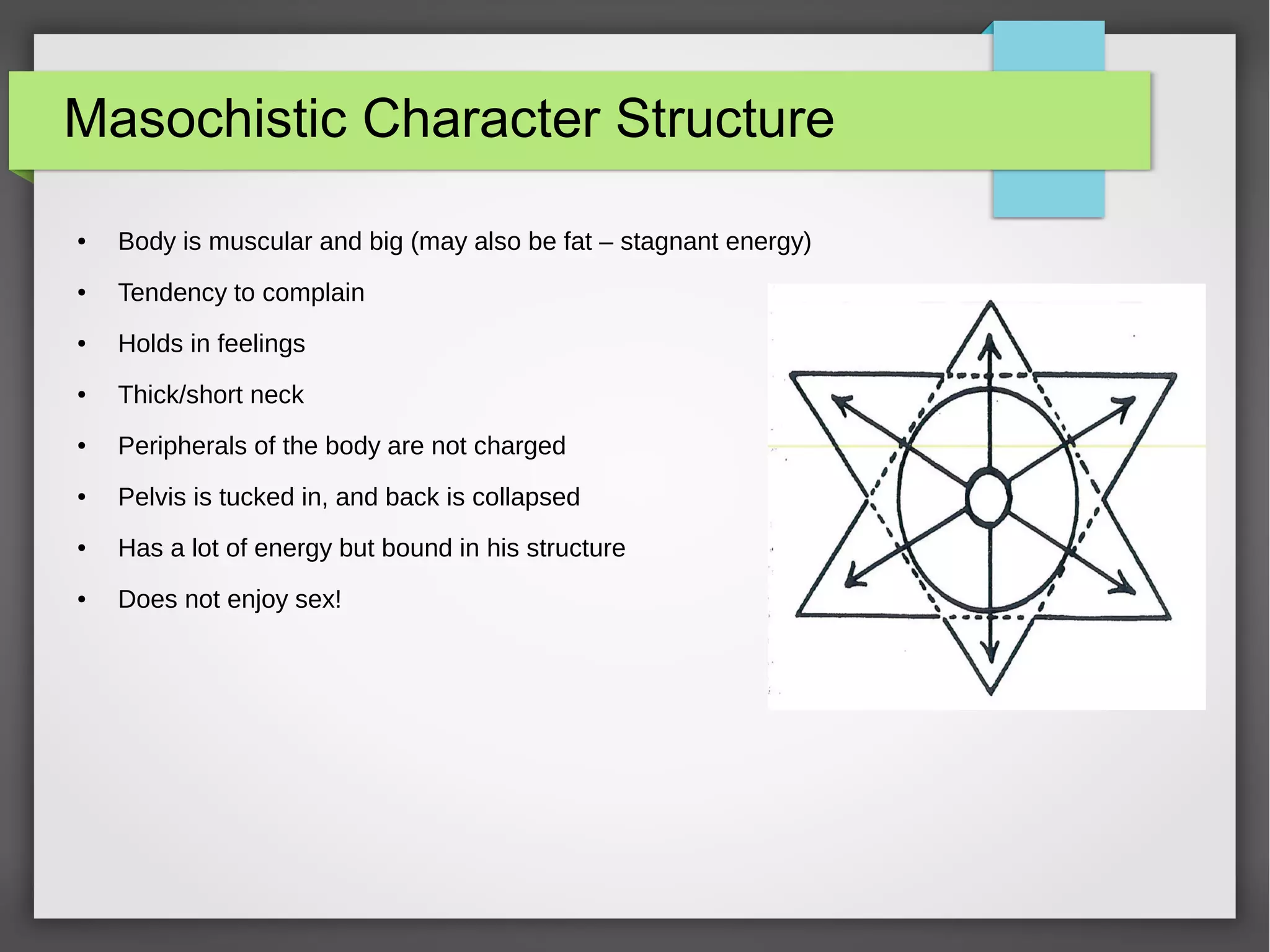
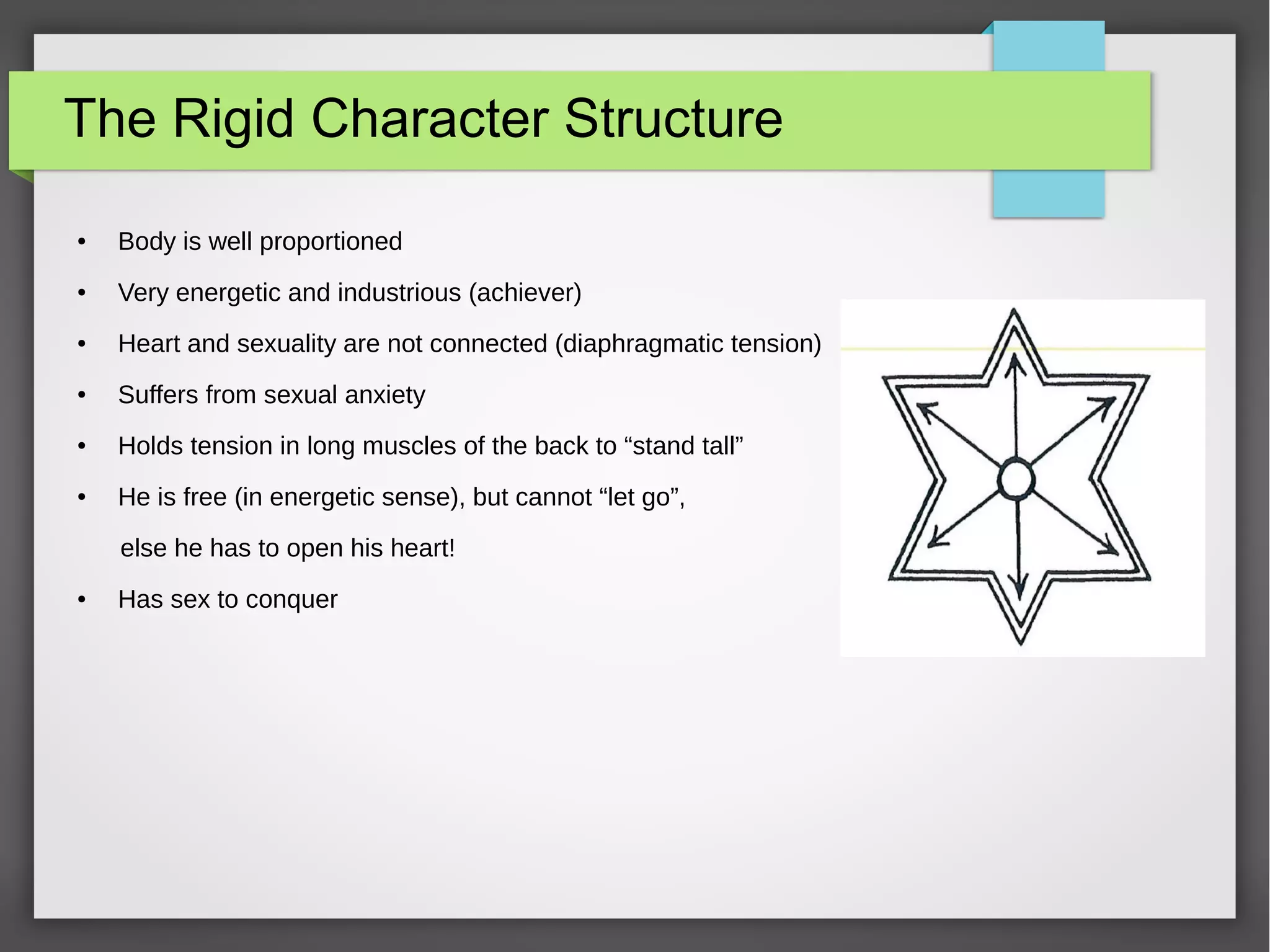
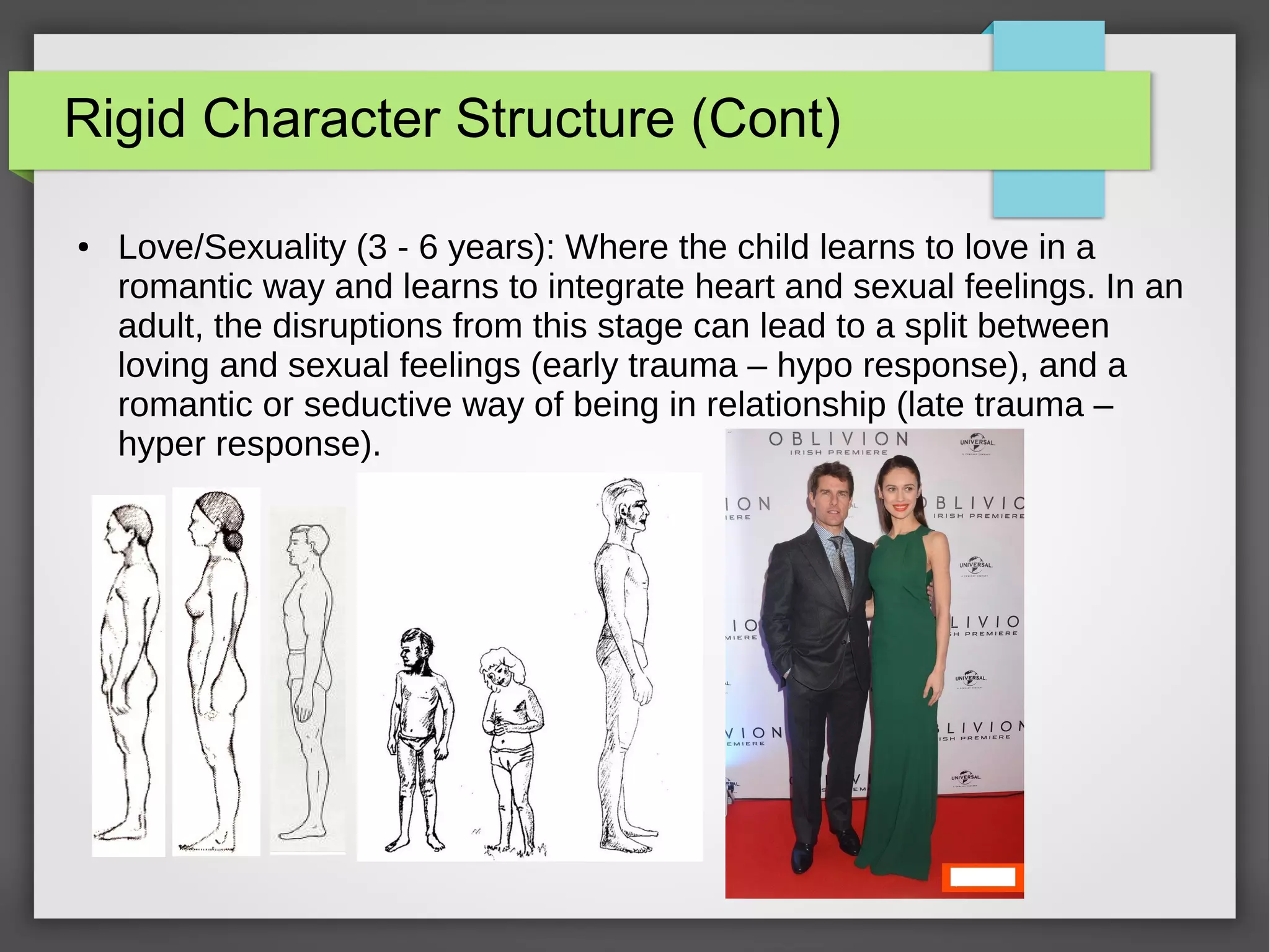
The document discusses developmental trauma and its impact on a child's growth and interaction with their environment, emphasizing the chronic effects of early unmet needs. It explores the concept of systems theory and how various character structures formed through developmental stages can result in specific psychological and physiological responses, leading to a distorted sense of self and difficulties in relationships. Key figures like Wilhelm Reich are referenced, highlighting how trauma shapes personal identity and behavior patterns.