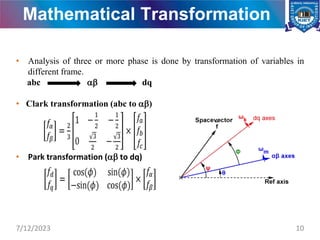
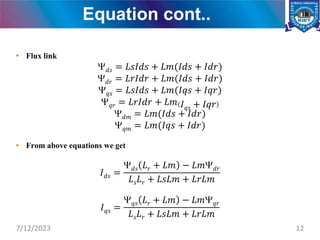
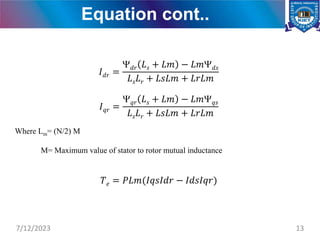
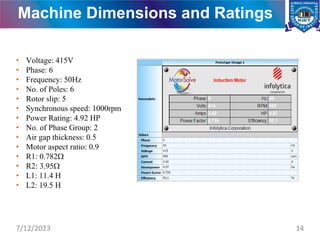
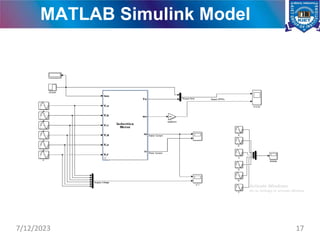
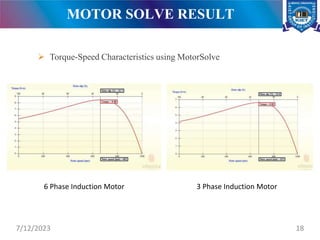
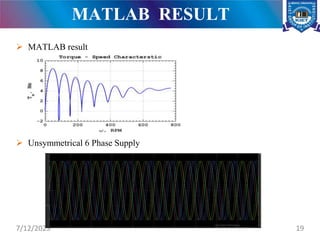
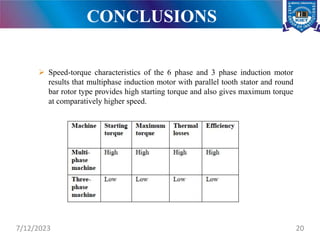
The document presents a project on the analysis and design of multiphase induction machines, detailing objectives such as reduced torque pulsation and improved reliability. It includes a literature review, methodology, and results indicating that multiphase machines can outperform traditional three-phase systems in various applications. Future research avenues are suggested, including electric propulsion systems and potential funding sources for further projects.





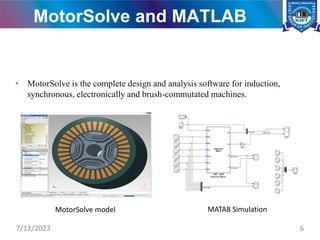

![Design of Six Phase IM
Induction motor design starts from stator design. Stator design depends
upon number stator slots.
General expression for number of stator slots is given by, S= n/2.p.[2+K]
Where S = no. of slots
n = no. of machine phases
p = no. of machine poles
For symmetrical ac winding: K = 0, 2, 4
For Asymmetrical ac winding: K = 1, 3, 5
In our case, number of poles = 6
7/12/2023 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-230712121847-7653f348/85/ANALYSIS-AND-DESIGN-OF-MULTIPHASE-INDUCTION-MACHINE-pptx-8-320.jpg)