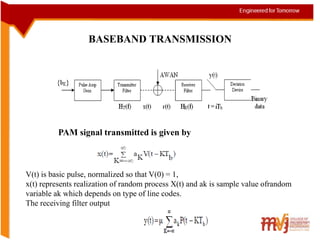
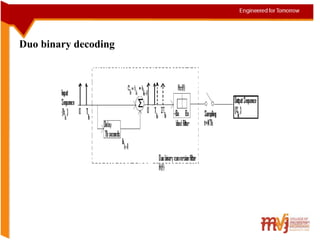
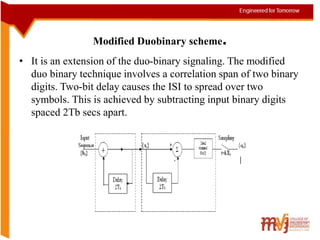
The document summarizes key concepts about intersymbol interference in baseband communication systems. It discusses Nyquist's criterion for distortionless transmission, correlative coding techniques like duo-binary coding to increase bandwidth efficiency, and the use of eye patterns and adaptive equalization to minimize intersymbol interference. The document also describes the basic elements of baseband PAM systems and how adaptive equalizers can continuously adjust their coefficients to compensate for channel dispersion during data transmission.