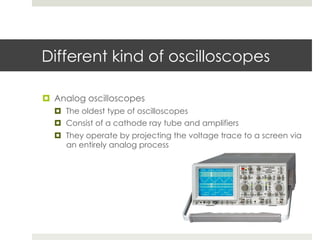
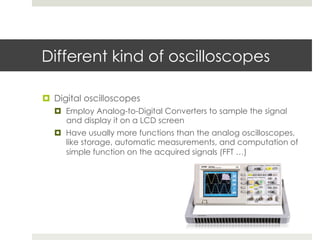
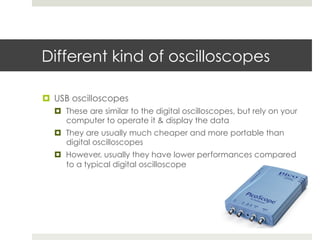
An oscilloscope is a key measurement device used to observe time-varying voltage signals across various fields such as engineering and medicine. There are three main types: analog oscilloscopes, digital oscilloscopes, and USB oscilloscopes, each with different functionalities and capabilities. Essential characteristics include bandwidth, which indicates the maximum measurable frequency, and sampling rate, determining the speed of data acquisition.