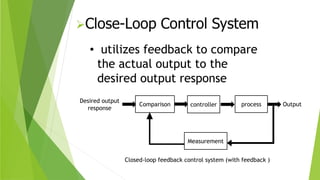
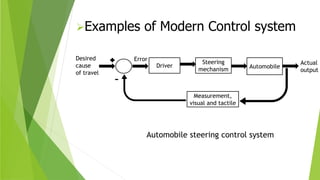
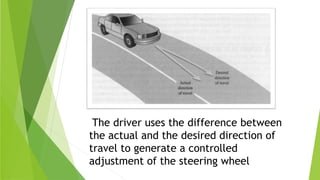
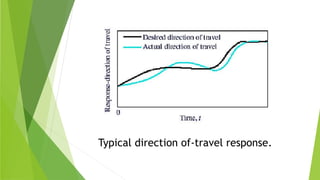
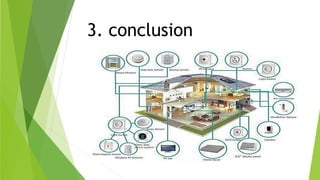
Control and monitoring systems are used to manage industrial processes. Control systems can operate as open-loop systems that actuate a process without feedback, or closed-loop systems that compare actual outputs to desired outputs using feedback to regulate the process. Modern examples include automobile steering control. Monitoring systems measure and store process data for analysis and alerting to document production quality over time.