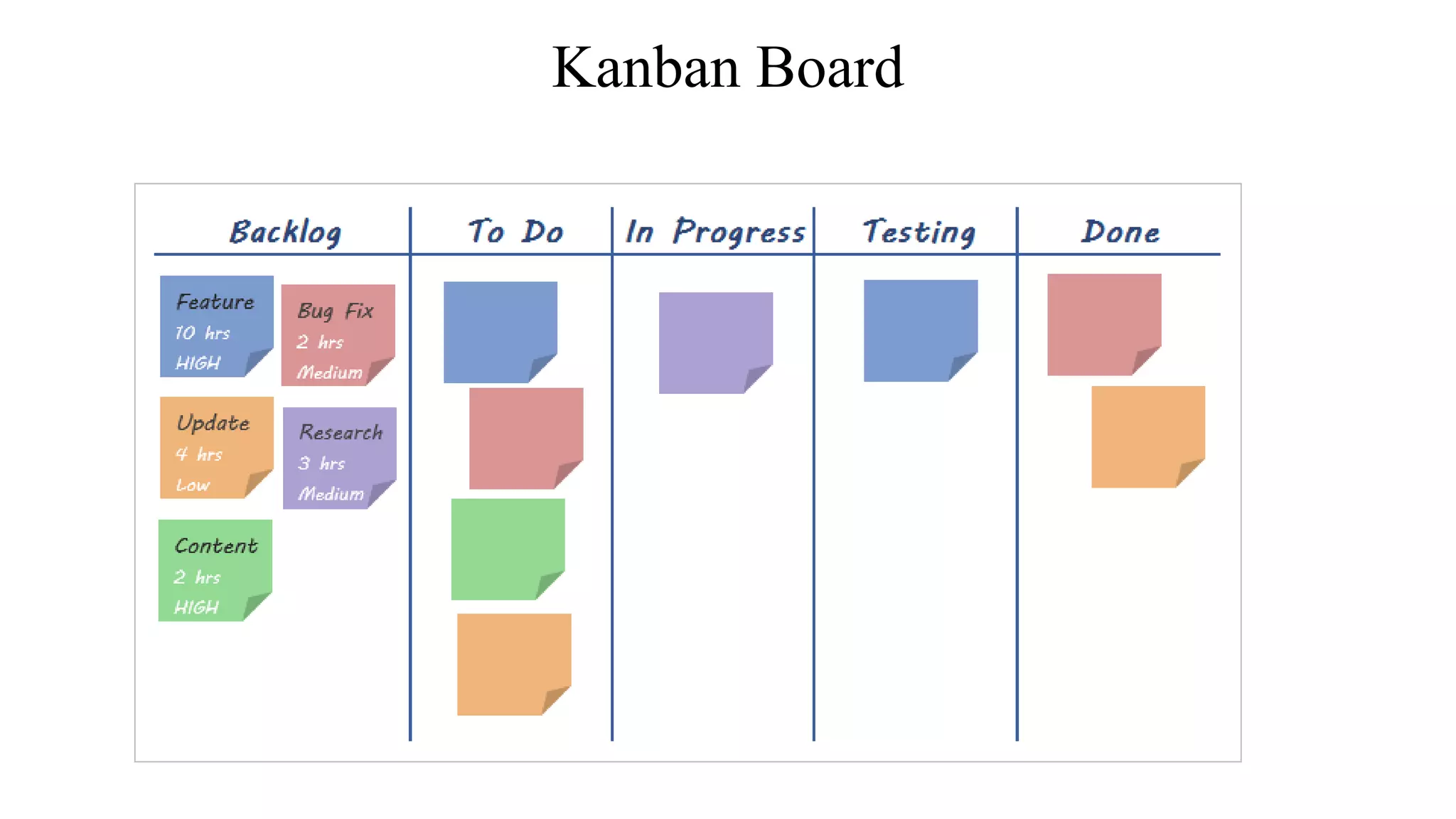
Kanban is a visual project management system originally used in Toyota's manufacturing process. It uses cards or images on a board to visualize workflow from one stage to the next and limit work-in-progress to avoid bottlenecks and focus on continuous flow. The core principles are to visualize workflow, limit WIP, focus on flow, and drive continuous improvement. Kanban and Scrum are both agile methods but Kanban allows continuous workflow while Scrum uses sprints and fixed roles. Key benefits of Kanban include improved visibility, collaboration, and productivity through waste reduction.