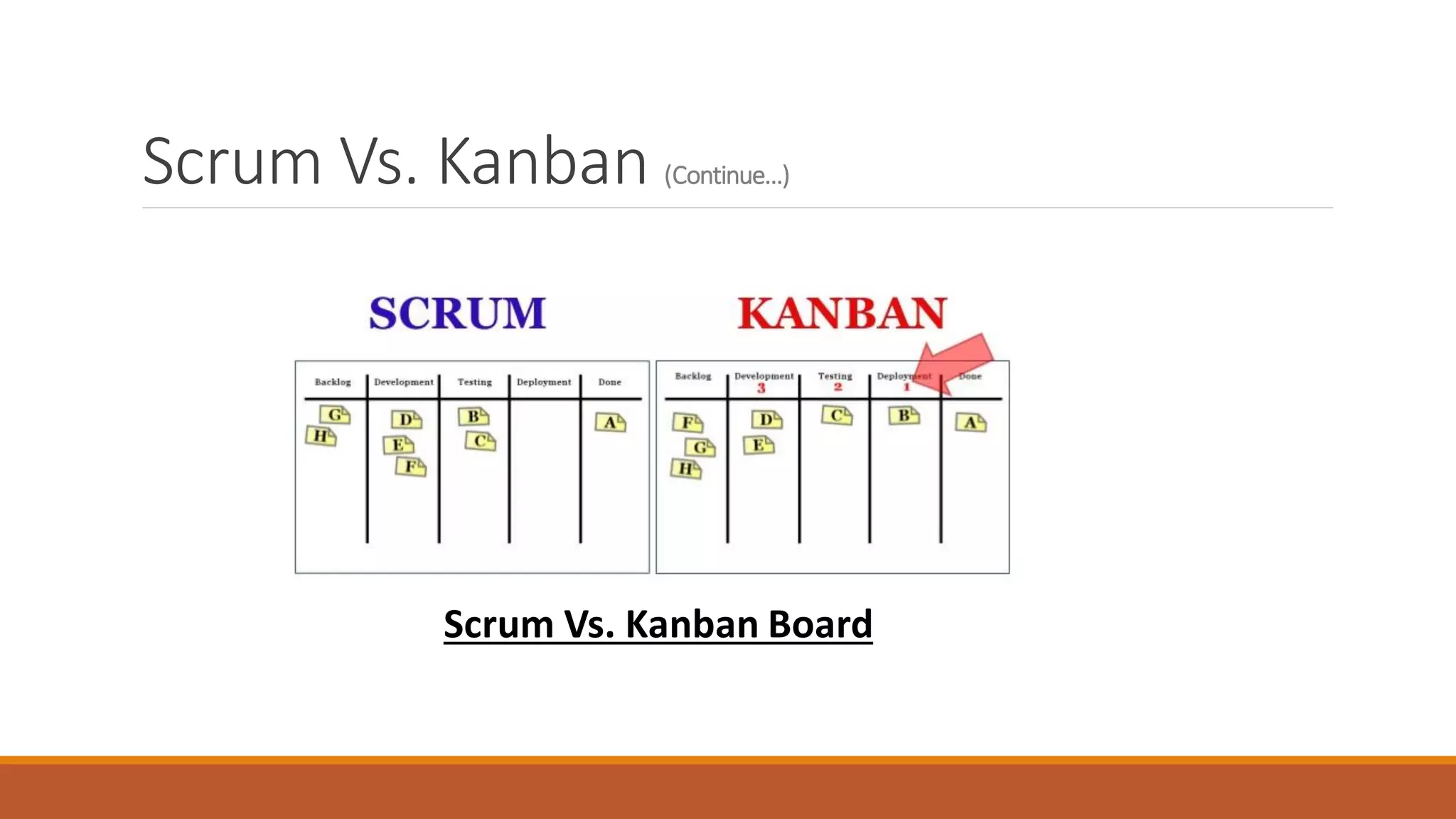
Scrum and Kanban are both agile project management methodologies. Scrum uses fixed length sprints to complete work in iterations, while Kanban uses a continuous flow approach. Some key differences are that Scrum requires timeboxing, estimation, and specific roles while Kanban is more flexible and focuses on limiting work in progress. Both aim to deliver work continuously and accommodate changes, with Scrum better for new products and Kanban for repetitive tasks. Metrics also differ, with Scrum using velocity and Kanban using lead time to measure delivery.