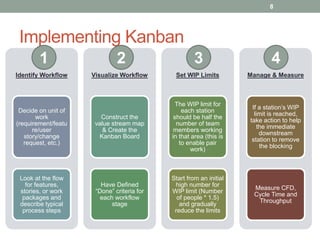
Kanban is a lean methodology for managing workflow. It uses visual cues like kanban boards to limit work-in-progress and focus on continuous flow. The document discusses (1) what Kanban is and how it differs from Scrum, (2) why organizations implement Kanban to improve flow and quality, and (3) where Kanban can be applied, including examples of kanban boards and tools for electronic tracking.