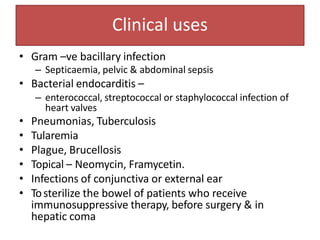
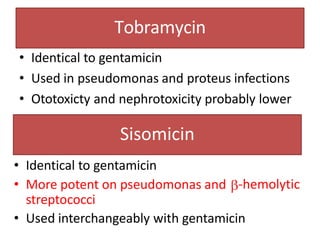
1. Aminoglycosides are a class of bactericidal antibiotics that interfere with protein synthesis in bacteria. They are effective against many gram-negative aerobic bacteria.
2. Their mechanism of action involves binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit and inducing misreading of mRNA, which breaks up polysomes.
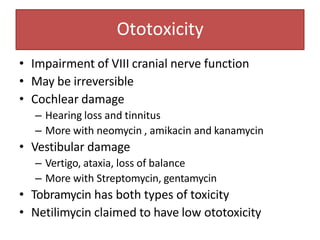
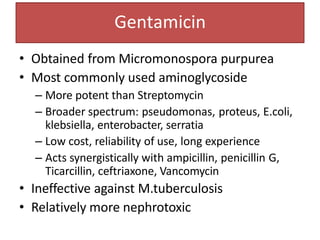
3. Their main toxicities include ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and neuromuscular blockade. Gentamicin is one of the most commonly used aminoglycosides.
















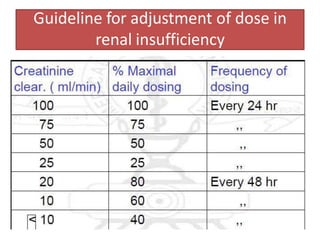
![Dose for a case of renal insufficiency
• Cockroft gault formula:
CrCl = (140-age) x weight [kg]
(sCr x 72)
– For females multiply above value by 0.85
• Corrected dose = Normal dose x pt CrCl
Normal CrCl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aminoglycosides-121209052919-phpapp02-221211142924-f5005f4b/85/aminoglycosides-121209052919-phpapp02-pptx-18-320.jpg)