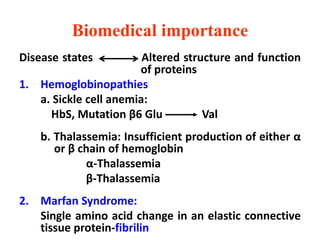
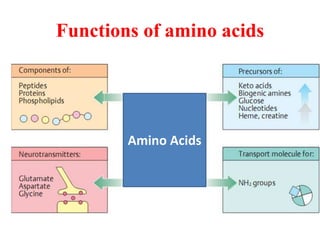
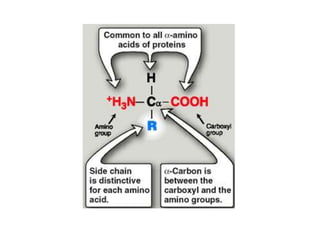
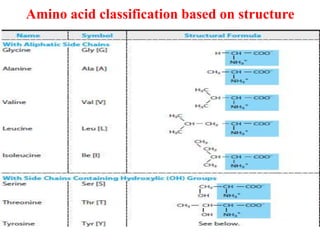
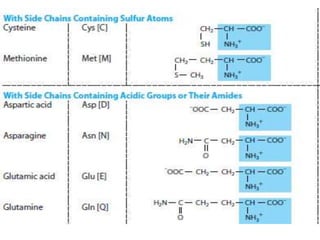
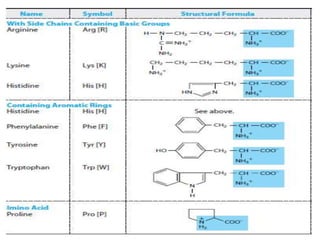
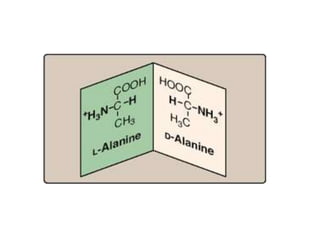
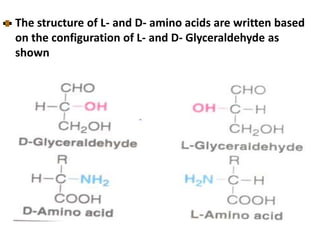
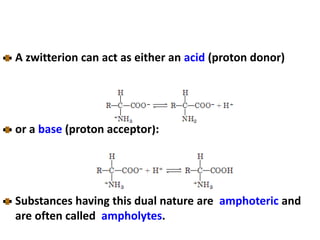
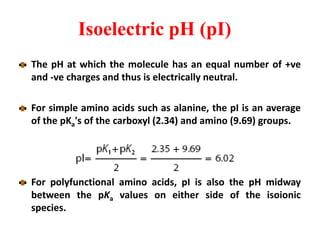
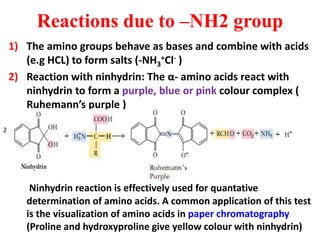
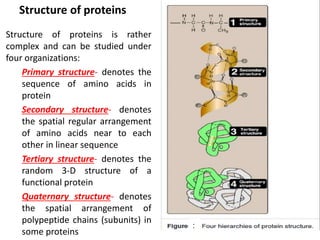
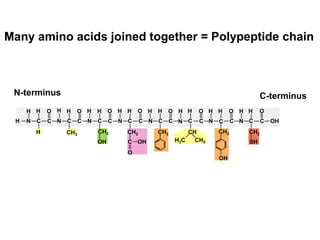
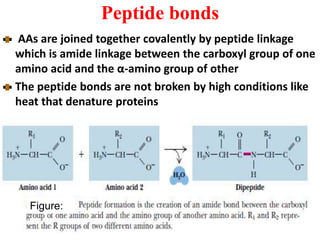
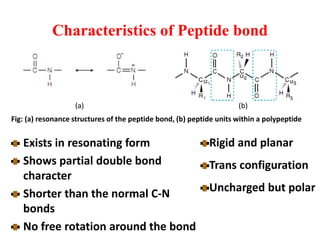
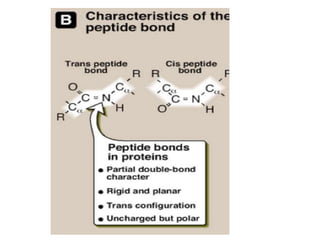
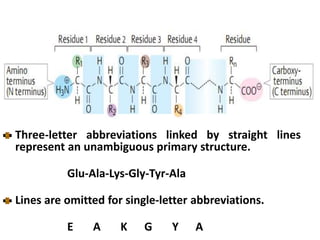
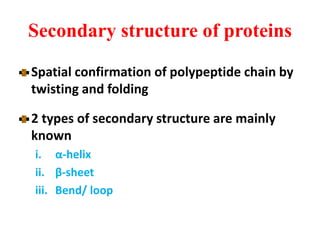
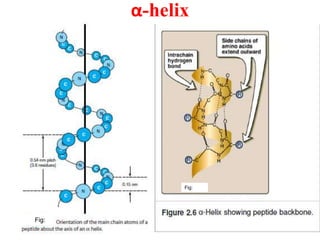
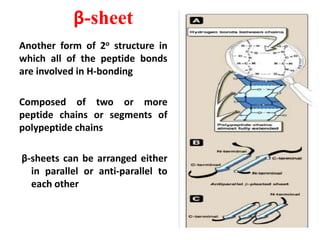
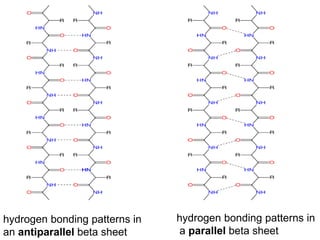
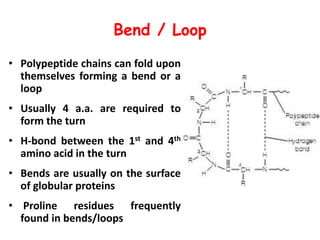
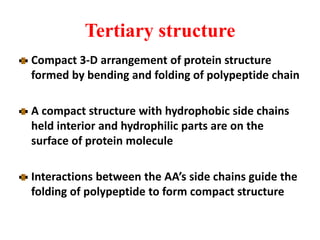
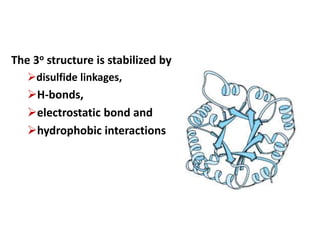
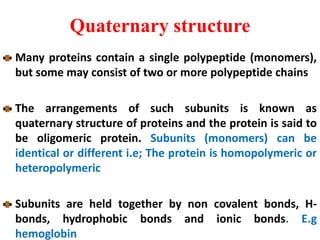
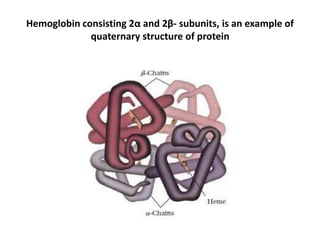
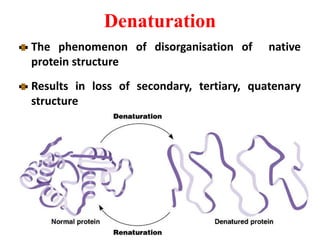
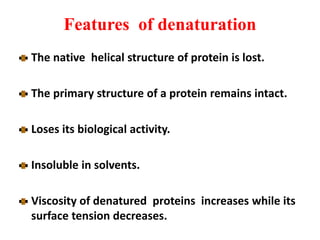
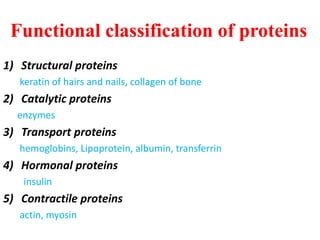
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 standard amino acids that make up the proteins in living organisms. Amino acids contain an amino group and a carboxyl group, and can be joined together via peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains. Proteins have complex structures with four levels of organization - primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. The primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. Secondary structures include alpha helices and beta sheets formed from regular patterns of hydrogen bonds between amino acids in the chain.