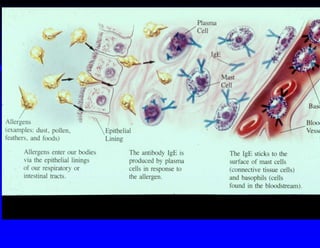
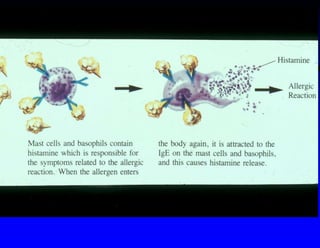
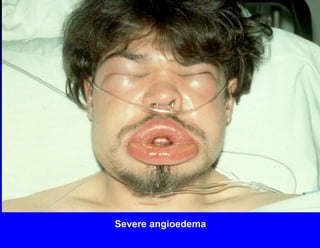
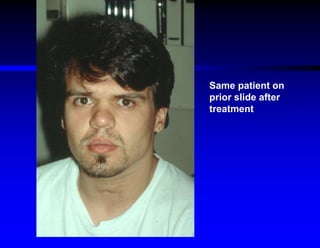
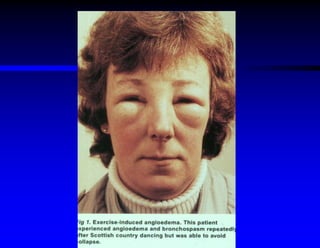
This document discusses hypersensitivity disorders and allergic emergencies. It defines anaphylaxis and anaphylactoid reactions, and describes the pathophysiology involving mast cell degranulation and the release of mediators like histamine. The key treatment for anaphylaxis is epinephrine, which causes vasoconstriction, bronchodilation and cardiac effects. Common causes of anaphylaxis include foods, medications like antibiotics and contrast dye, and hymenoptera stings. Airway management and monitoring are important in the emergency department.