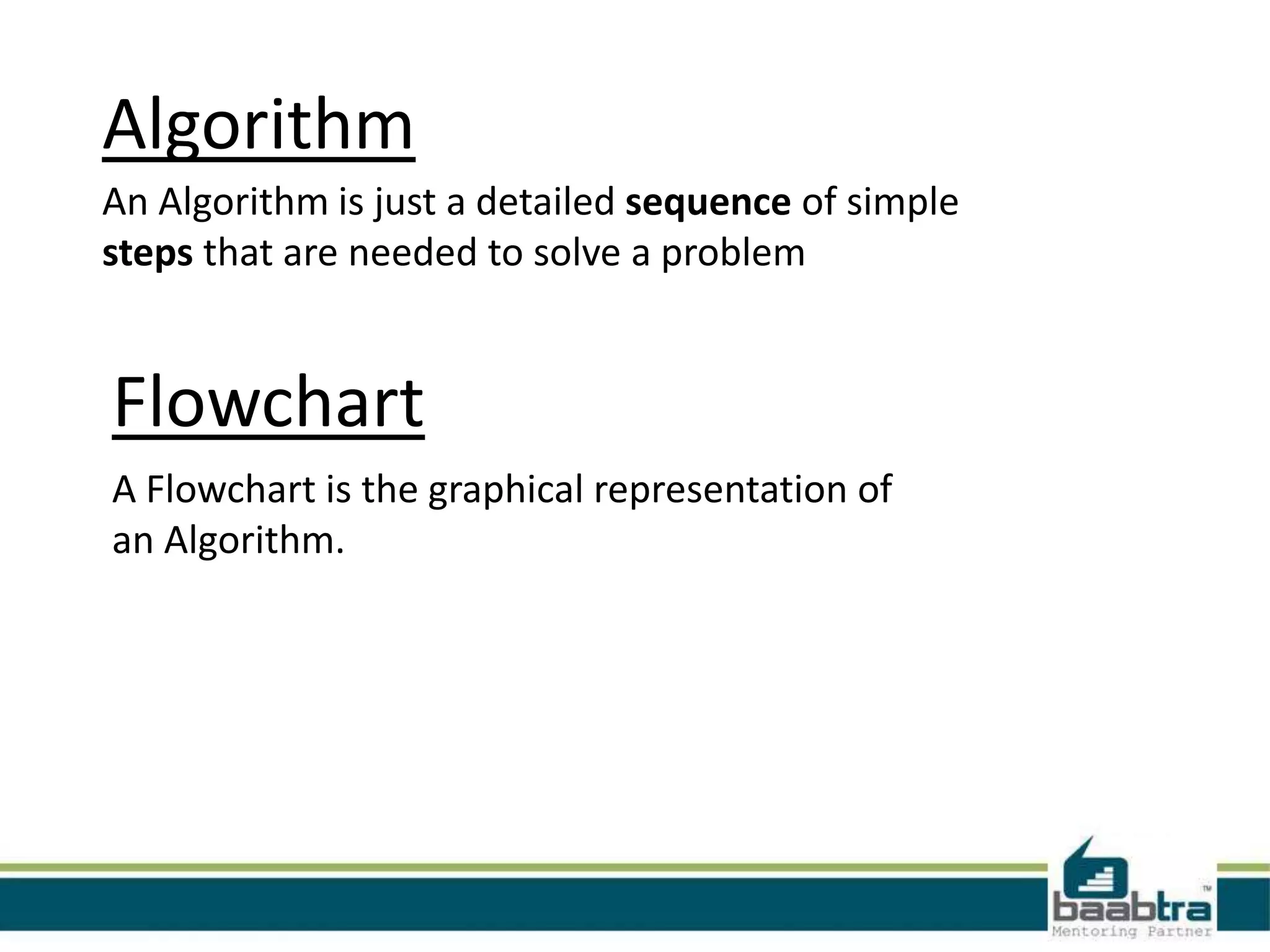
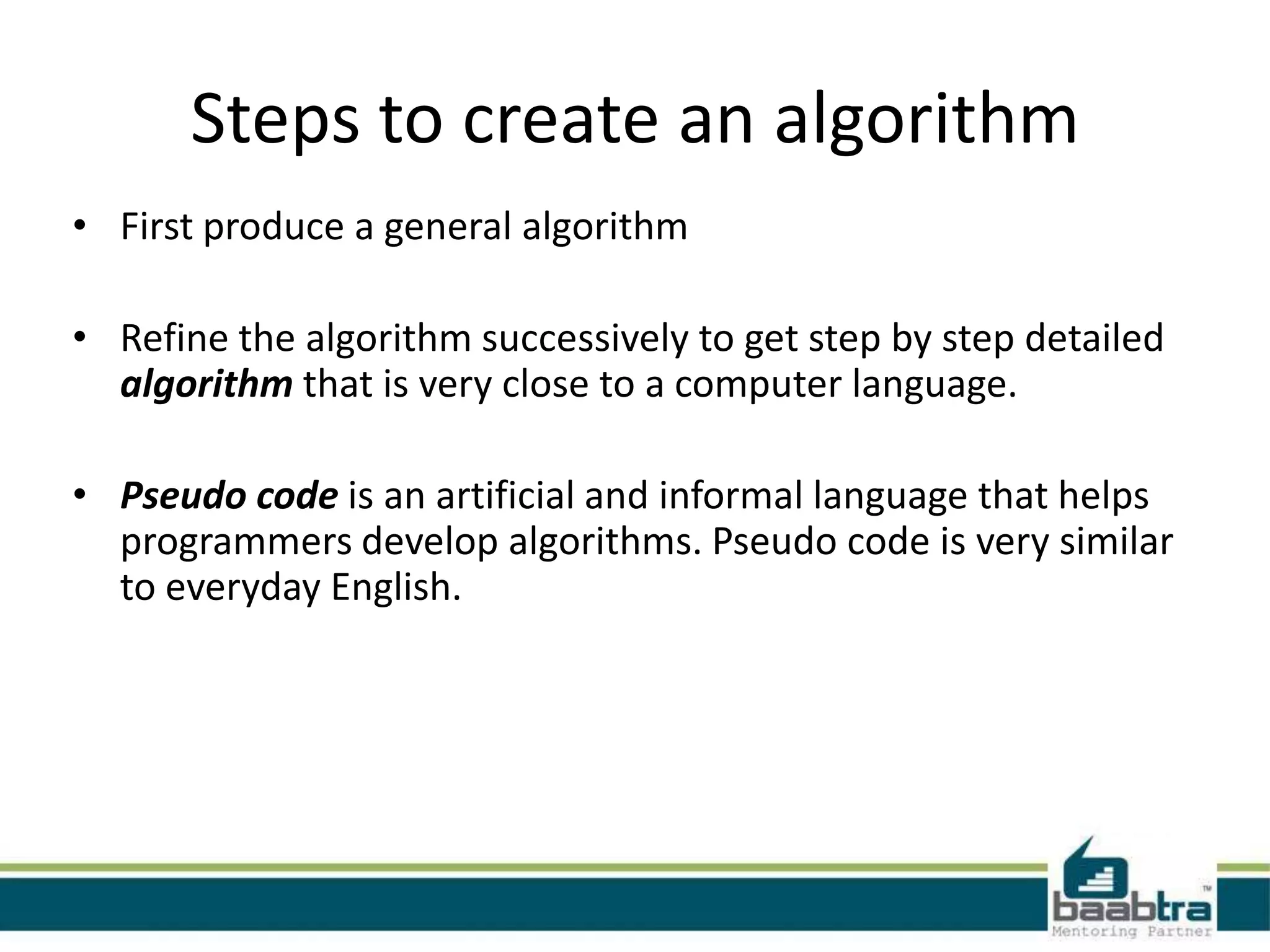
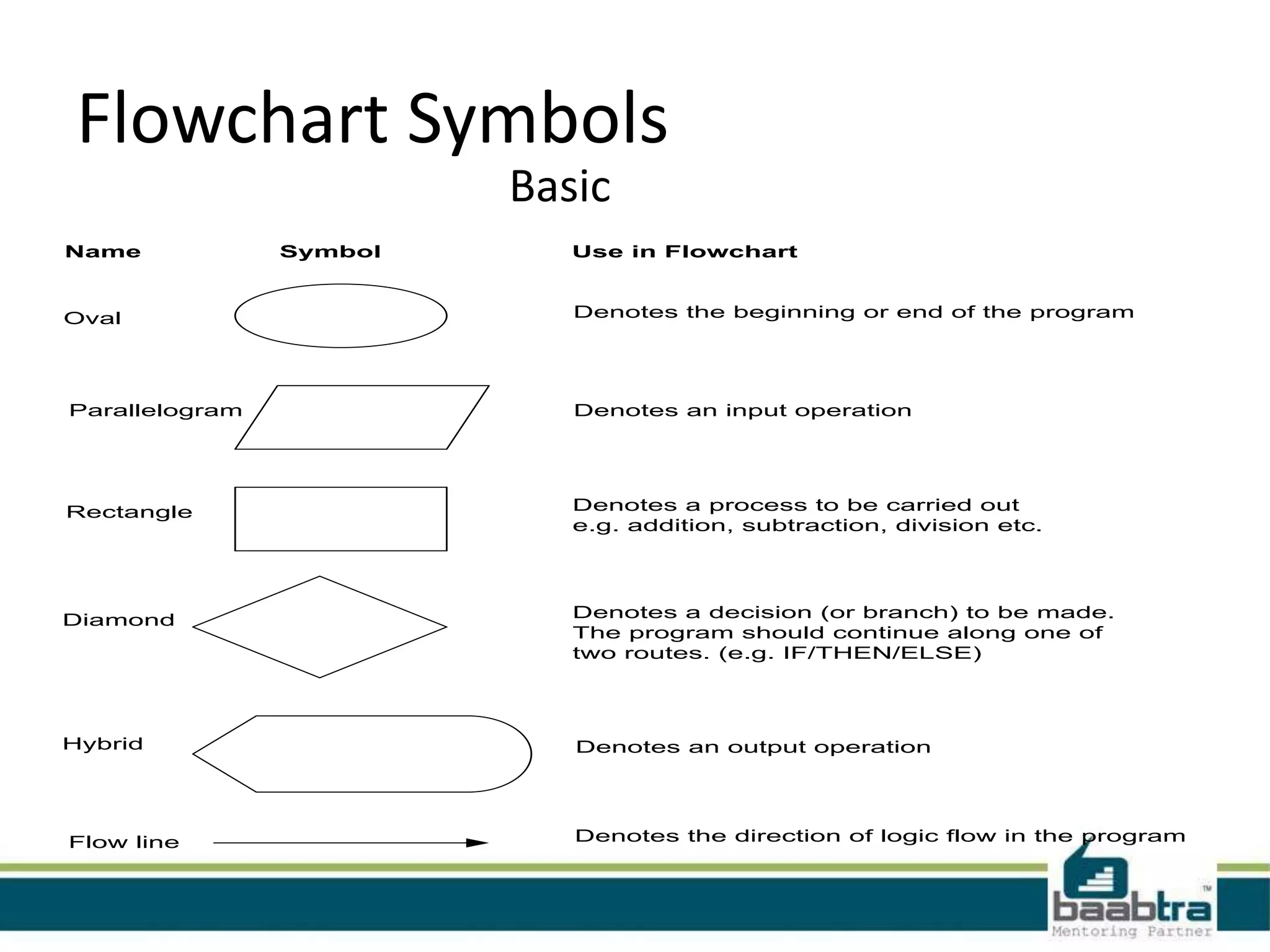
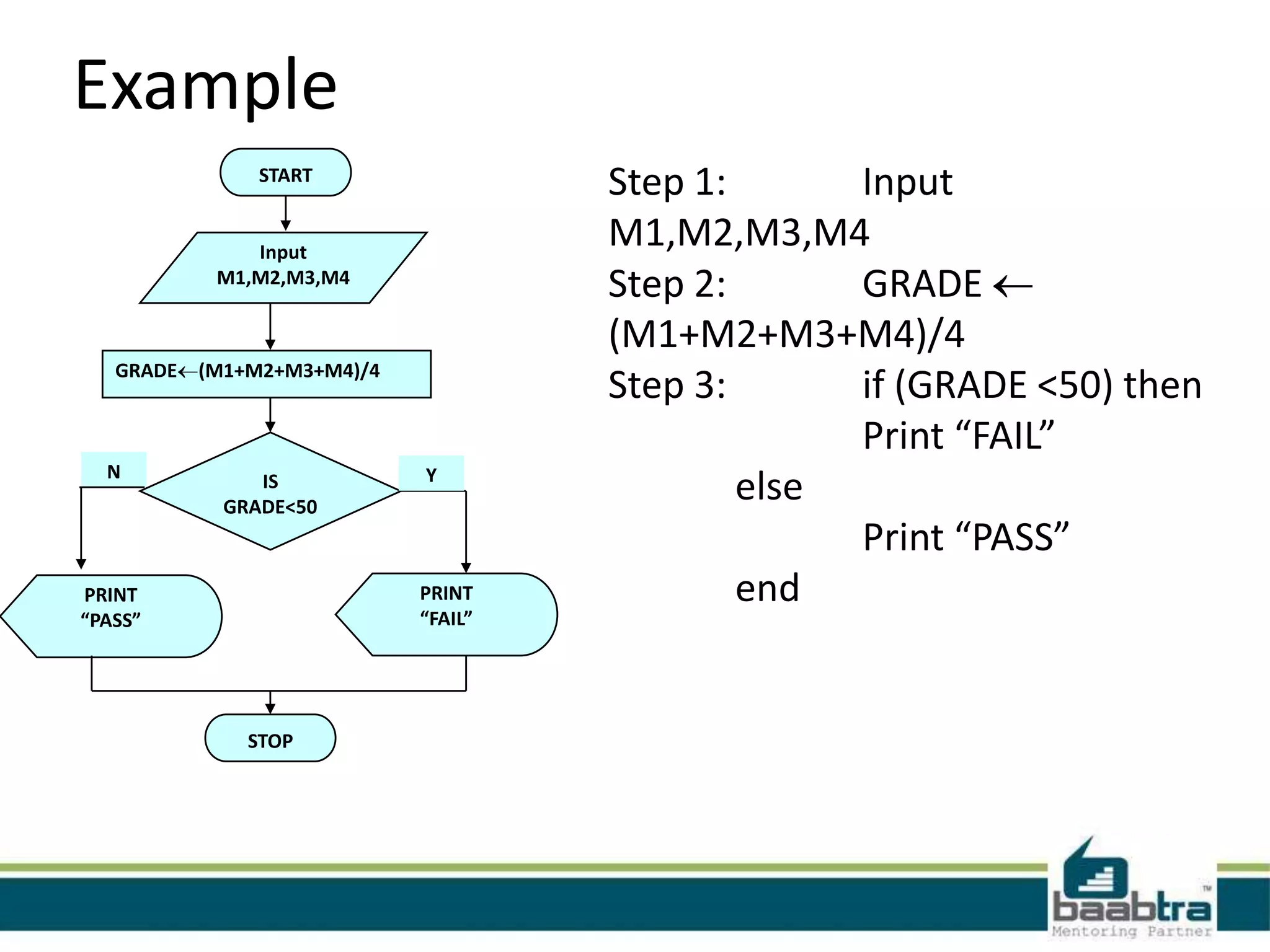
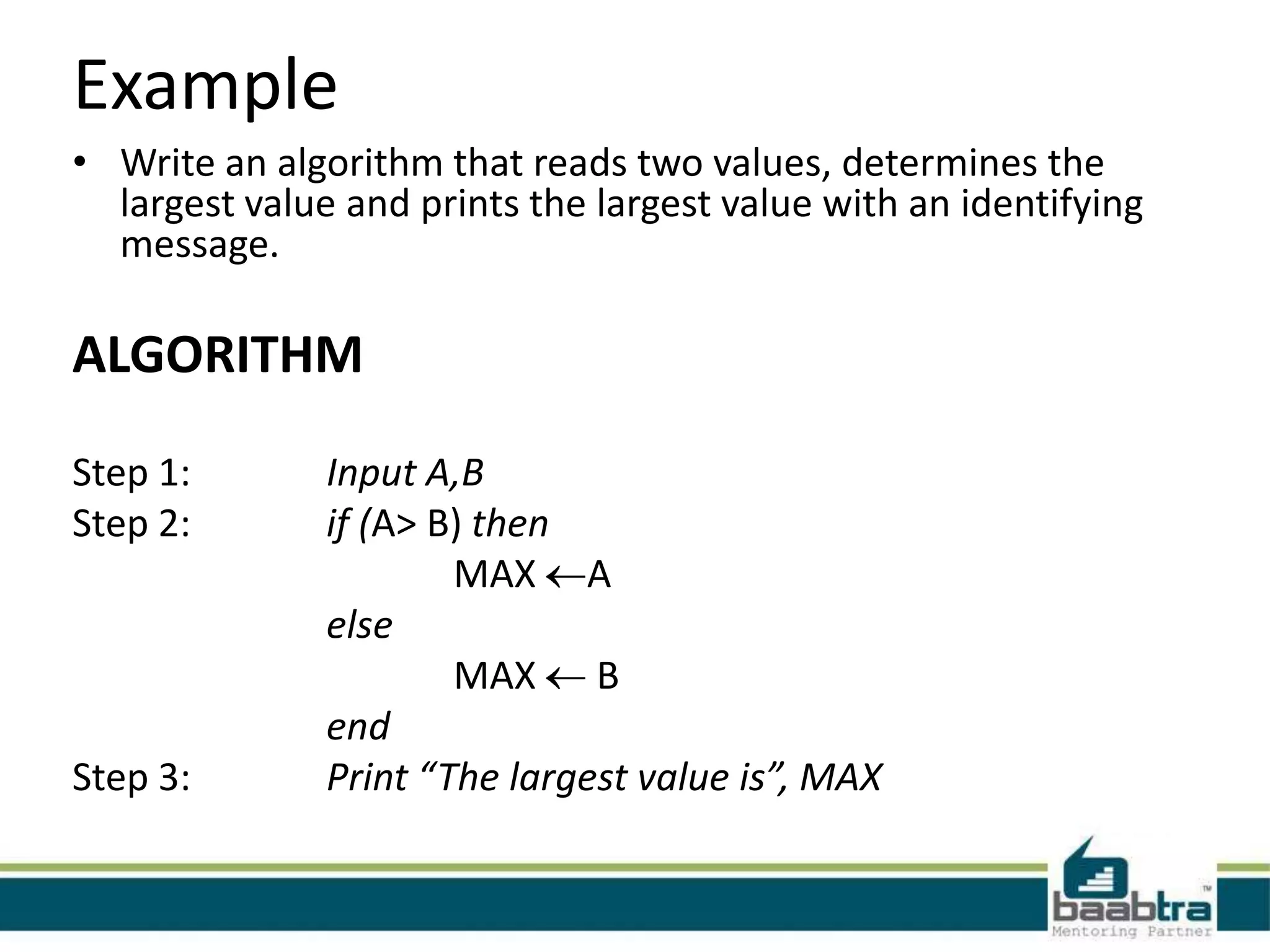
The document defines algorithms and flowcharts. It provides an example algorithm to determine a student's final grade and whether they pass or fail based on calculating the average of four marks. It then shows the same algorithm expressed as a flowchart using common flowchart symbols like rectangles, diamonds, and arrows. Another example algorithm determines the largest of two values and prints the result. The document encourages visiting the presenter's Facebook page and websites for more information.