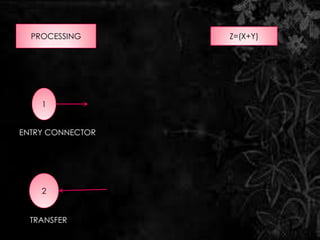
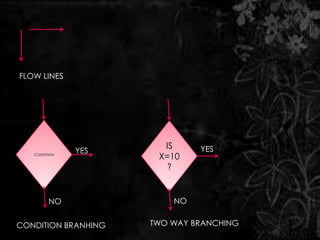
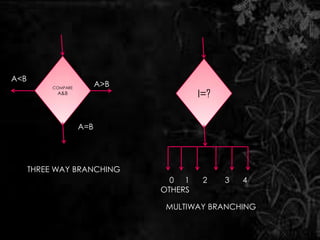
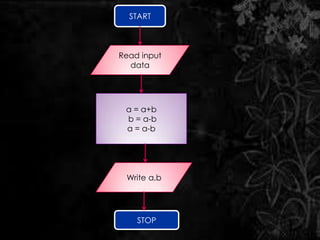
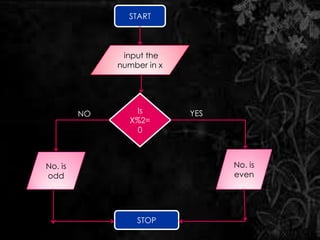
The document discusses flow charts, which are graphical representations of problem-solving processes. Flow charts use different shapes to represent instruction types and should convey the main logic from left to right and top to bottom. They allow for effective problem-solving, coding, debugging, and testing but take more time to draw and can be difficult to change. The document provides examples of flow charts, including one to swap two numbers without a third variable and one to determine if a number is even or odd.