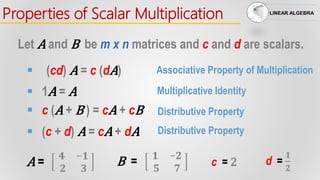
The document provides a comprehensive overview of linear algebra, focusing on properties of matrix operations including addition, scalar multiplication, and multiplication. It details properties such as commutativity, associativity, and the identity elements relevant to matrices, as well as the properties of the zero matrix. Additionally, it discusses the behavior of matrices similar to real numbers and introduces the concept of identity matrices and transposes.









![LINEAR ALGEBRA
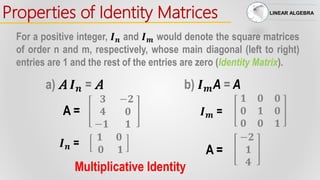
Properties of Identity Matrices
𝑰 𝟏 =
For a positive integer, 𝑰 𝒏 would denote the square matrix of
order n whose main diagonal (left to right) entries are 1 and
the rest of the entries are zero (Identity Matrix).
𝟏 𝟎
𝟎 𝟏
𝑰 𝟑 =
𝟏 𝟎 𝟎
𝟎 𝟏 𝟎
𝟎 𝟎 𝟏
[𝟏] 𝑰 𝟐 =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalreportinlinearalgebra-180311062317/85/Algebraic-Properties-of-Matrix-Operations-11-320.jpg)