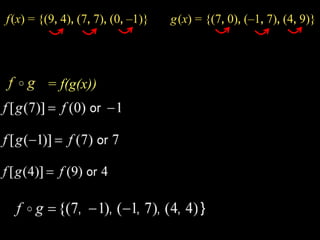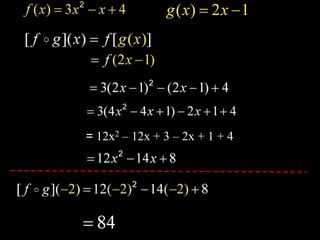Embed presentation
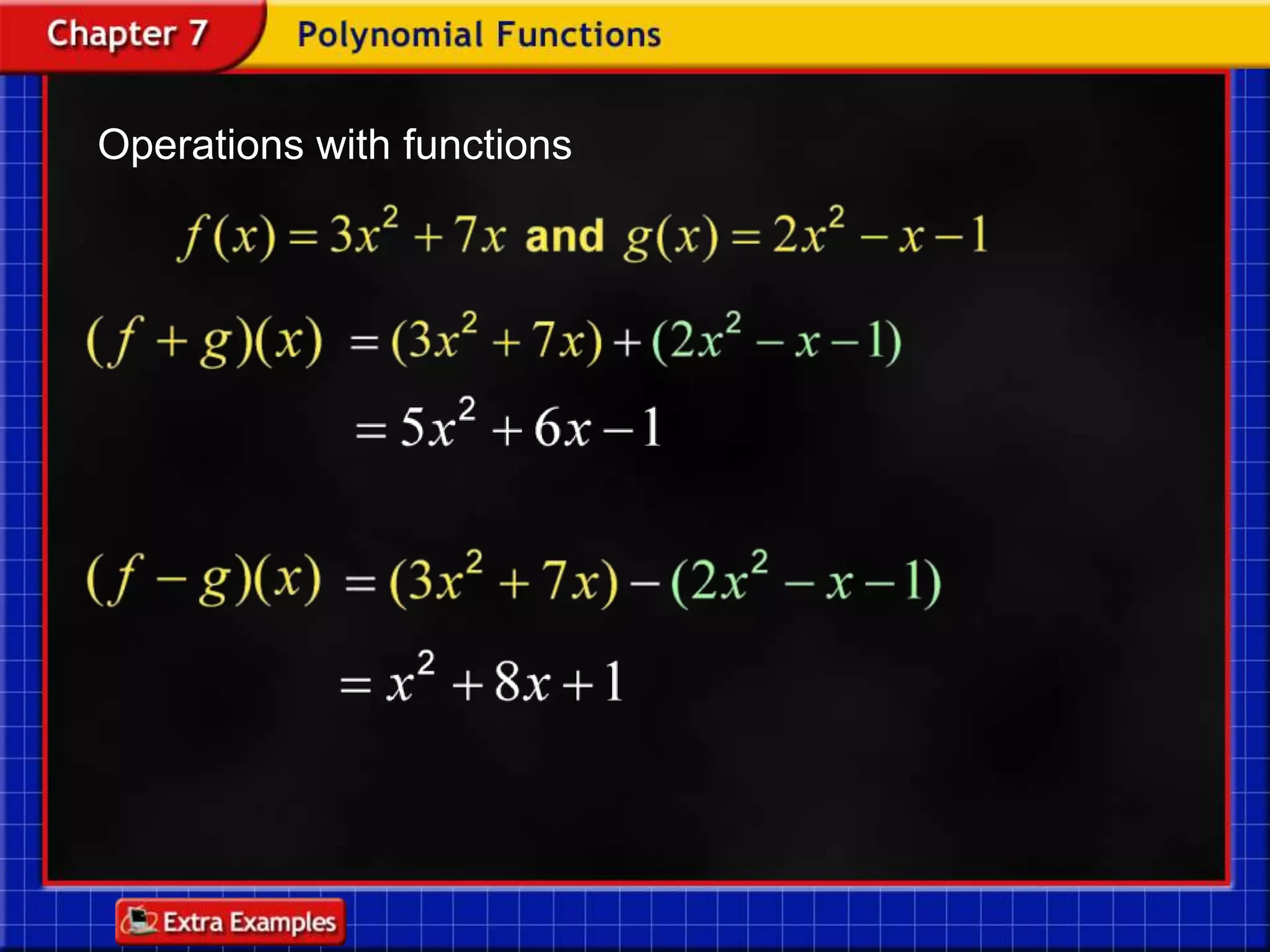
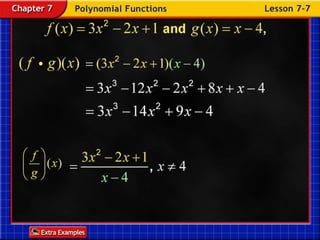
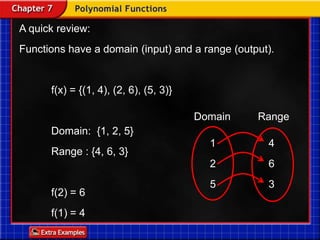

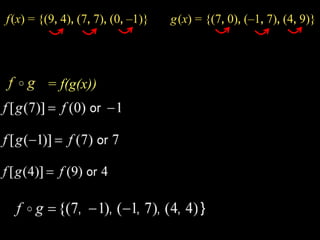
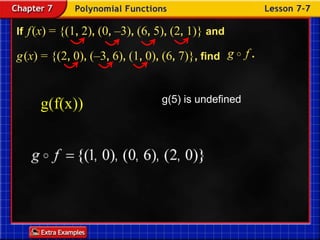
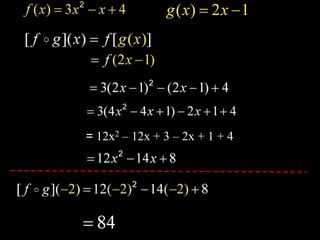
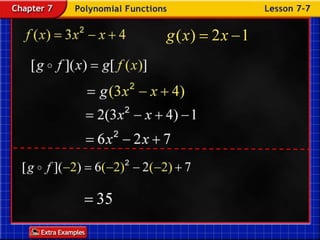
Functions take an input and return an output. Composite functions combine multiple functions by making the output of one function the input of another. For example, if f(x) is defined as x^2 and g(x) is defined as x + 1, then the composite function g(f(x)) would be x^2 + 1. To evaluate a composite function, you first apply the inner function f(x) and then apply the outer function g(x) to the result.