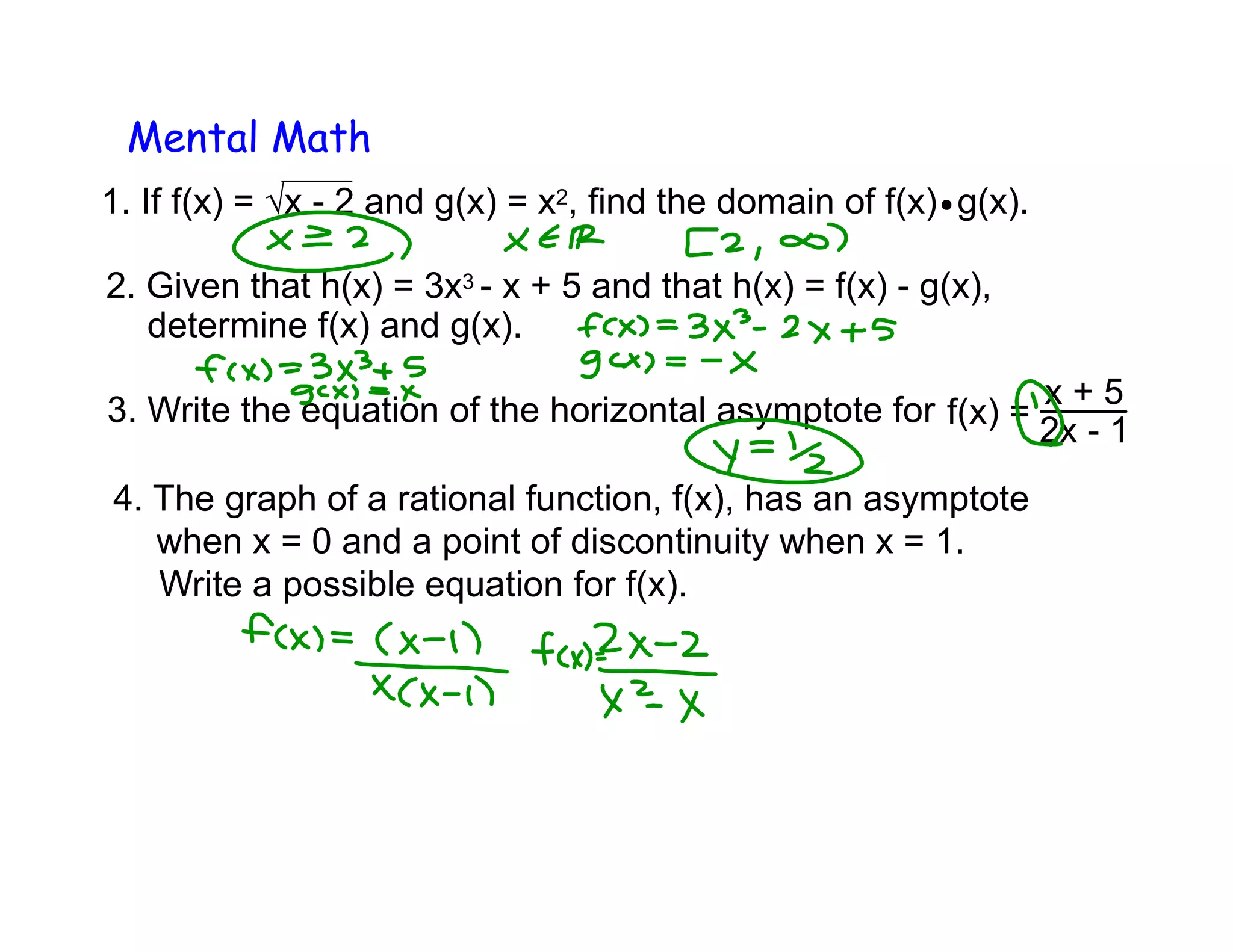
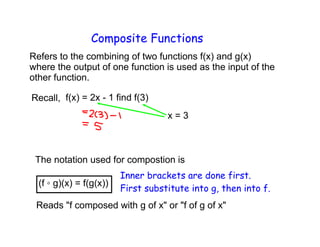
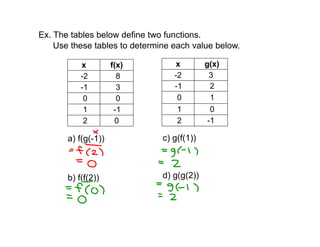
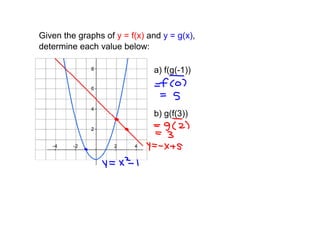
1. The document discusses composite functions, which involve combining two functions f(x) and g(x) where the output of one is used as the input of the other. It provides examples of evaluating composite functions using tables and graphs.
2. Key steps for evaluating composite functions are: 1) Substitute the inner function into the outer function and 2) Simplify the expression. Order matters as f(g(x)) and g(f(x)) may have different values.
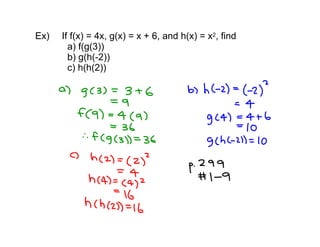
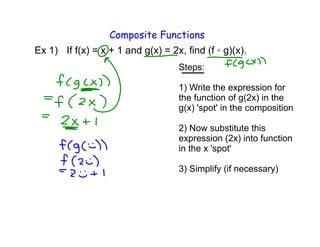
3. Examples are worked through to find composite functions given basic functions like f(x) = x + 1 and g(x) = 2x as well as more complex rational functions.