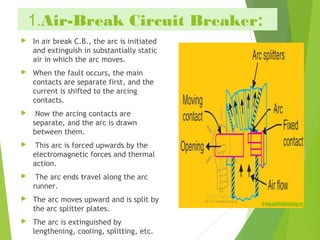
The document discusses air circuit breakers, detailing their definitions, construction (both external and internal), operation principles, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It explains that air circuit breakers operate in atmospheric pressure and have replaced oil circuit breakers due to safety concerns. Key points include the working mechanism of arc interruption, types of air circuit breakers (air break and air blast), and their uses in electrical protection systems.