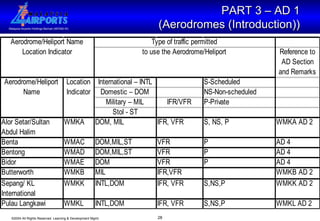
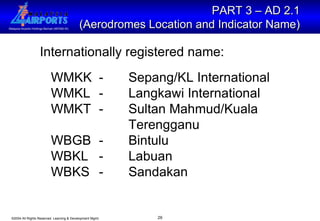
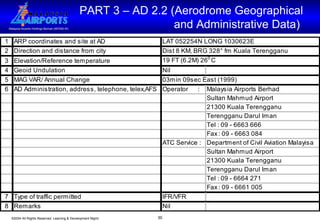
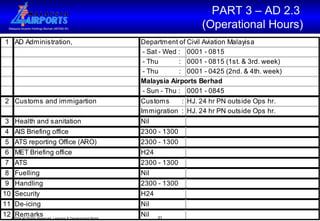
The document discusses the Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP), which provides essential aeronautical information to pilots and air navigation. It describes the AIP's content and structure, including general information (GEN), en-route information (ENR), and aerodrome information (AD). The AIP is published by contracting states and contains permanent information as well as information on procedures and regulations. Aerodrome operators are responsible for providing accurate data to the AIP.




































![If I am good tell others if not tell me! Technical Services Division Malaysia Airports Holdings Berhad Sultan Abdul Aziz Shah Airport 47200 Subang Selangor Tel. No: 603 7840 7231 e-mail: [email_address] .com.my Need more info?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aip-operations-basic-training-020904-1231920240945709-1/85/AIP-Operations-Basic-Training-020904-56-320.jpg)
