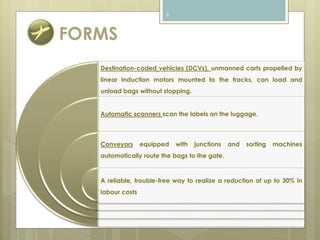
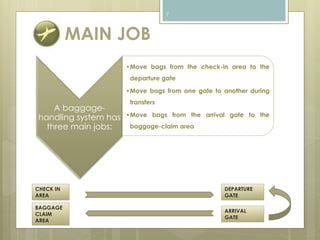
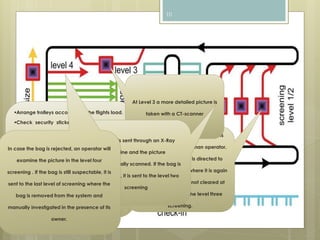
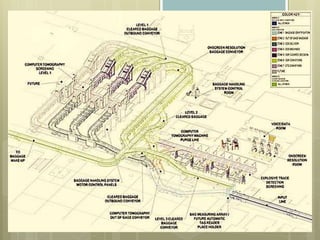
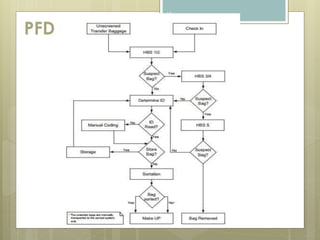
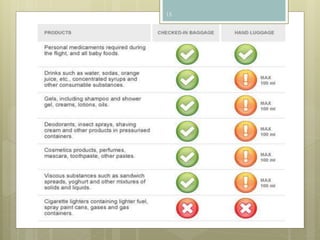
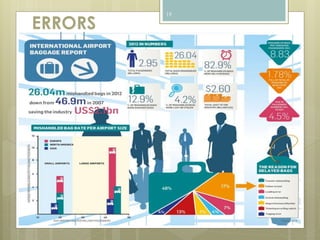
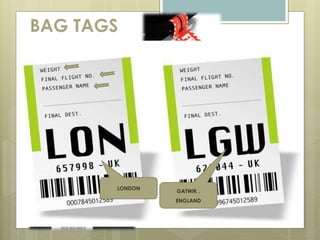The document discusses baggage handling systems at airports. It describes how baggage handling systems transport checked luggage from ticket counters to airplanes and from airplanes to baggage claims. The systems perform functions like bag detection, volume regulation, load balancing, bag counting, tracking, and redirection. They have three main jobs - moving bags from check-in to departure gates, between gates during transfers, and from arrival gates to baggage claims. The document also outlines the basic processes that bags go through and how the systems work to sort bags to their proper destinations.