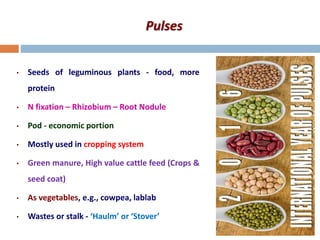
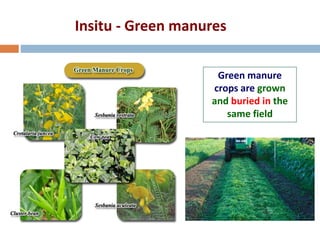
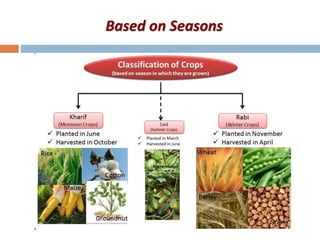
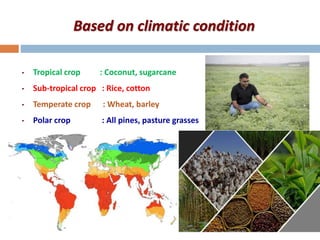
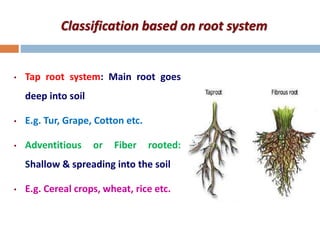
This document discusses different ways of classifying crops in agronomy. It describes how crops can be classified based on their life cycle as annual, biennial or perennial crops. It also discusses classifications based on economic use, seasons, climate, root system, photosynthesis pathways, photoperiod requirements, and more. Key classifications mentioned include cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, fibers crops, fodder crops, spices and condiments. Common examples are provided for each classification type.