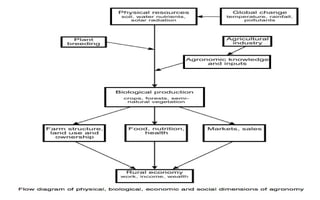
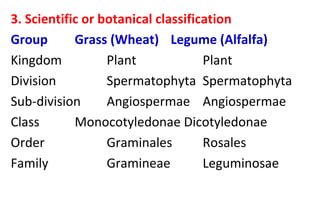
Agronomy is the study of crop production and soil management. It involves identifying suitable cultivation seasons, applying fertilizers and herbicides, managing water, implementing new technologies, and maintaining ecological balance. Agronomy is related to other agricultural sciences like soil science, crop physiology, and plant ecology. Crops are classified in various ways for better understanding, including by their life cycle (annual, biennial, perennial), economic use (cereals, millets, pulses, oilseeds), and botanical traits. The major crops grown in India are classified based on season (kharif, rabi, summer) and climate (tropical, sub-tropical, temperate, polar).