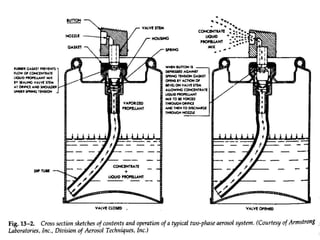
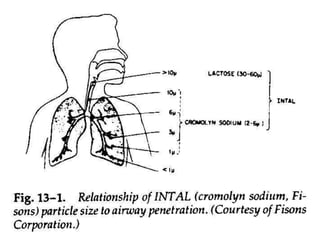
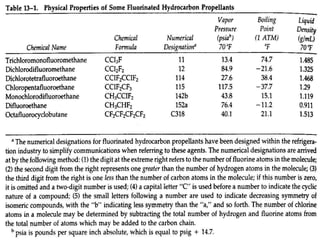
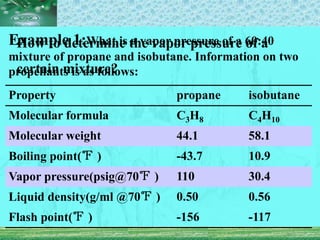
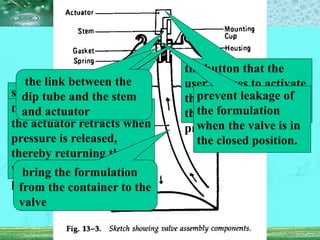
Pharmaceutical aerosols are pressurized dosage forms that emit fine dispersions of liquid or solid active ingredients for local or systemic drug delivery. They consist of a product concentrate and a propellant, with various filling methods used to combine the ingredients under pressure within metal, glass, or plastic containers fitted with valve assemblies. Aerosols offer advantages like controlled dosing and non-invasive administration, but also have disadvantages like higher costs and potential for irritation.