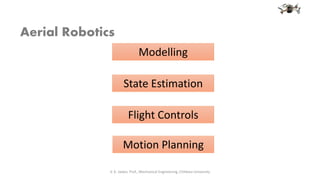
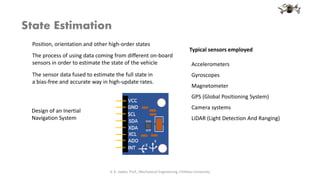
The document discusses aerial robotics and is presented by Vijay Kumar, a professor of mechanical engineering at Chitkara University. It introduces the topics of remotely piloted vehicles, unmanned aerial vehicles, drones and their use of four rotors powered by independent motors. It also discusses modelling, state estimation, flight controls, motion planning and the dynamics of aerial robotics.