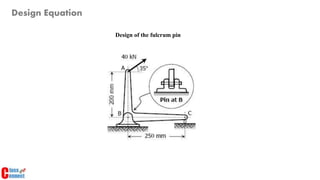
1. The document discusses the development of design equations for machine members.
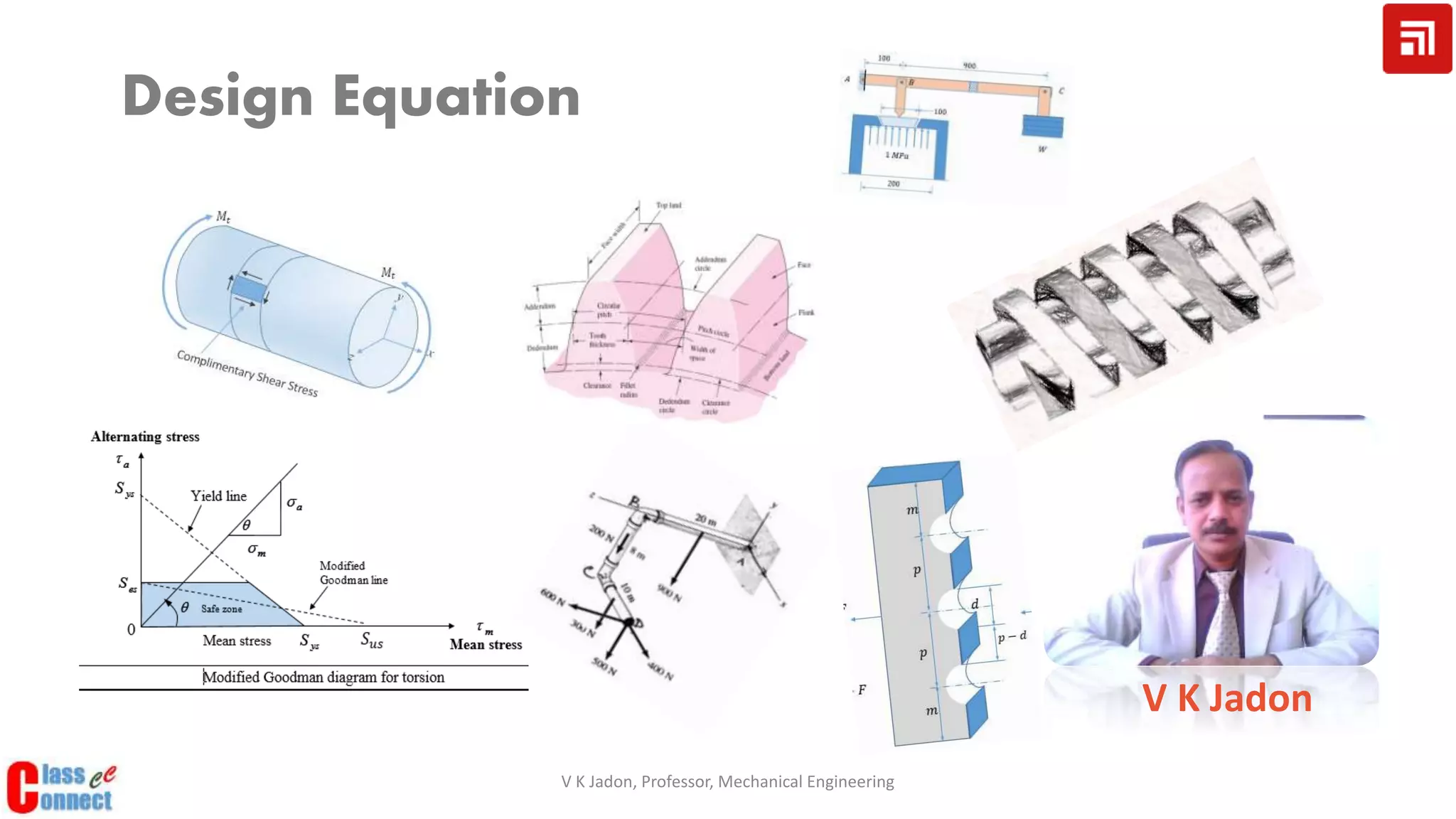
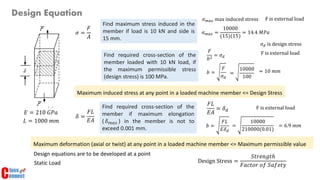
2. Maximum induced stress at any point in a loaded machine member must be less than or equal to the design stress. Maximum deformation must also be less than the maximum permissible value.
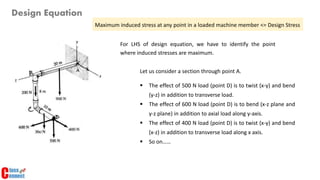
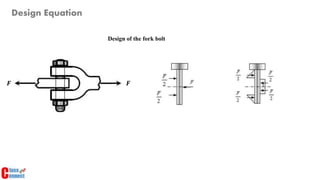
3. Developing design equations requires identifying the point of maximum stress and considering how loads are transferred between members in an assembly.