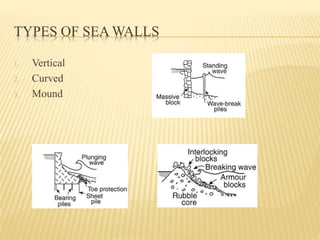
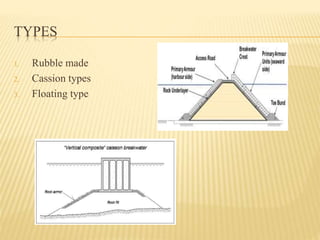
This document discusses various advanced technologies for coastal protection in India. It introduces the importance of protecting India's long coastline from flooding and erosion. It then describes different methods of coastal protection including sea walls, breakwaters, groins, gabions, revetments, bulkheads, and beach nourishment. It provides details on each method and examples of their use. The document emphasizes the importance of coastal protection for safety, economic, and environmental reasons. It notes that development and habitat loss threaten coastlines and that protection methods should consider social, economic and environmental impacts.