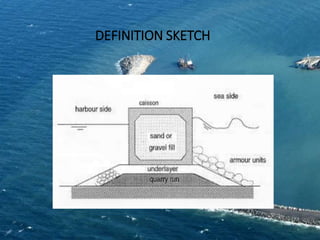
This document discusses different types of breakwaters. Breakwaters are structures built along coasts to protect areas from wave disturbance. There are three main categories: rubble mound breakwaters, vertical-wall breakwaters, and floating breakwaters. Rubble mound breakwaters are constructed from natural rubble or stone and are the most widely used in Indian ports due to their cost-effectiveness. Vertical-wall breakwaters use concrete blocks or mass concrete and reflect waves without dissipating much energy. Floating breakwaters are removable structures constructed from caissons or pontoons that can be sunk or floated as needed.