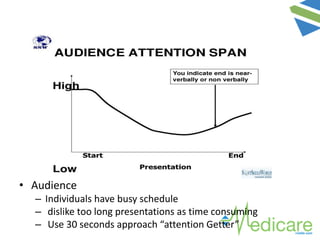
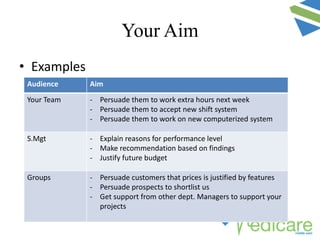
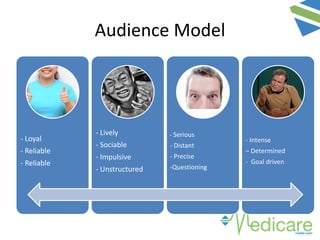
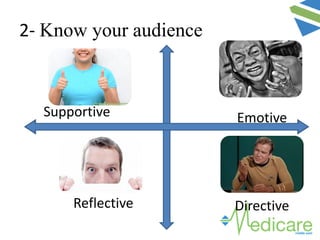
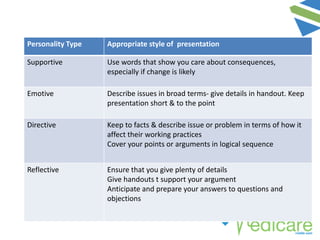
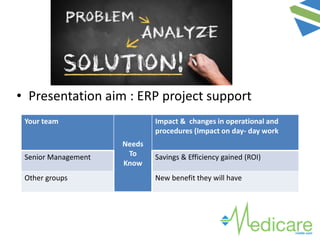
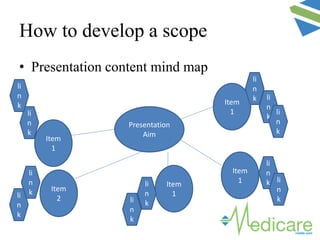
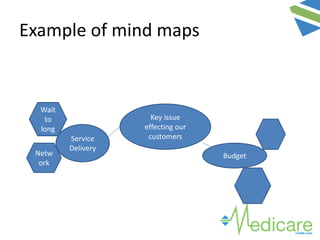
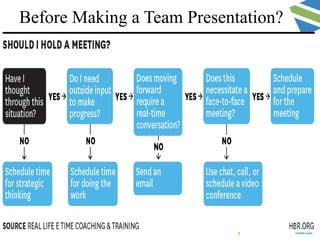
The document provides guidance on advanced presentation skills, outlining how to create an effective aim statement, understand audience types, and structure presentation content. It emphasizes the importance of tailoring presentations to different audience groups, whether they be teams, senior management, or external entities, while also offering tips on preparation and delivery. Key points include planning the scope of the presentation, knowing the audience's needs and preferences, and ensuring clarity in communication.