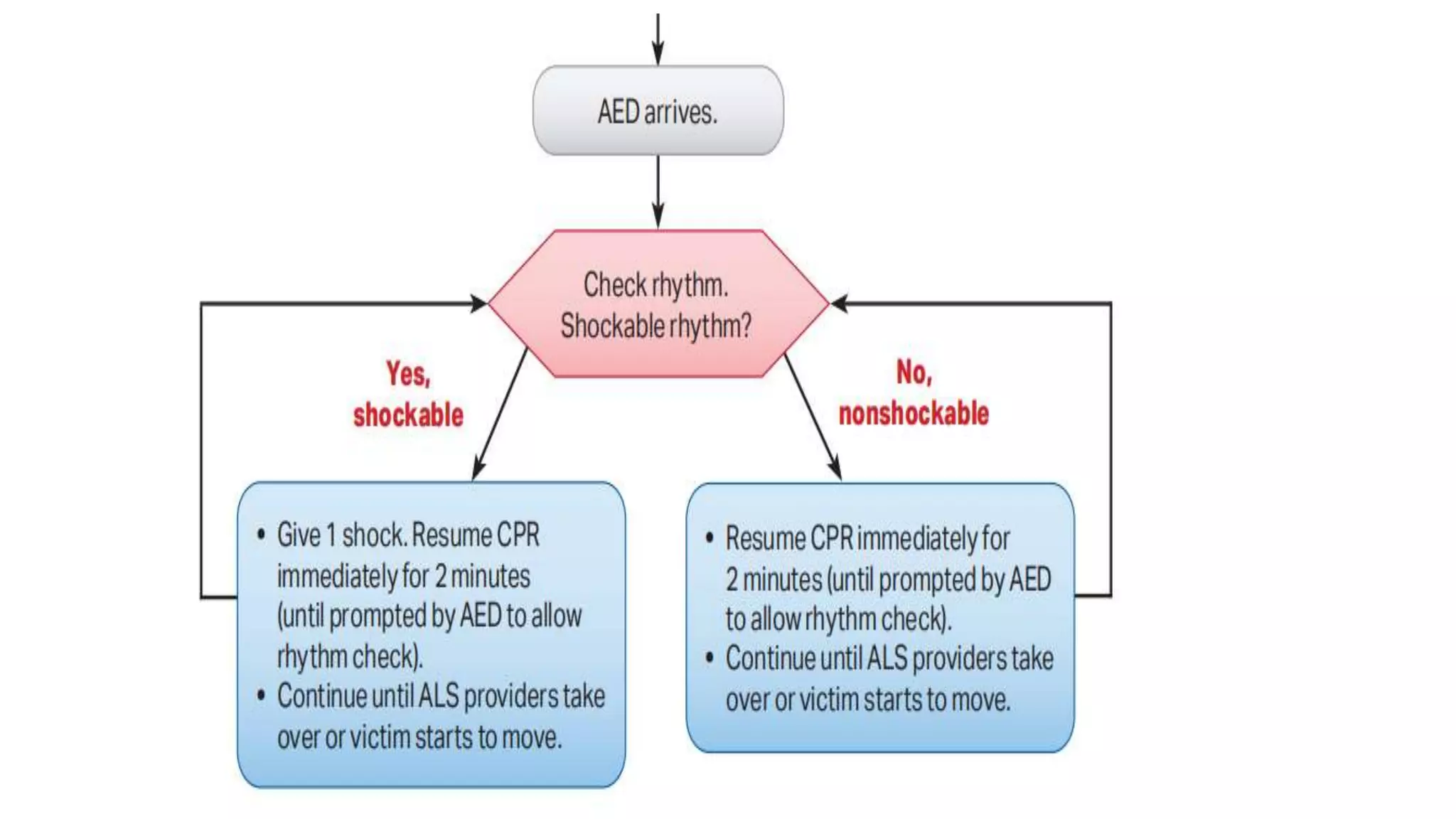
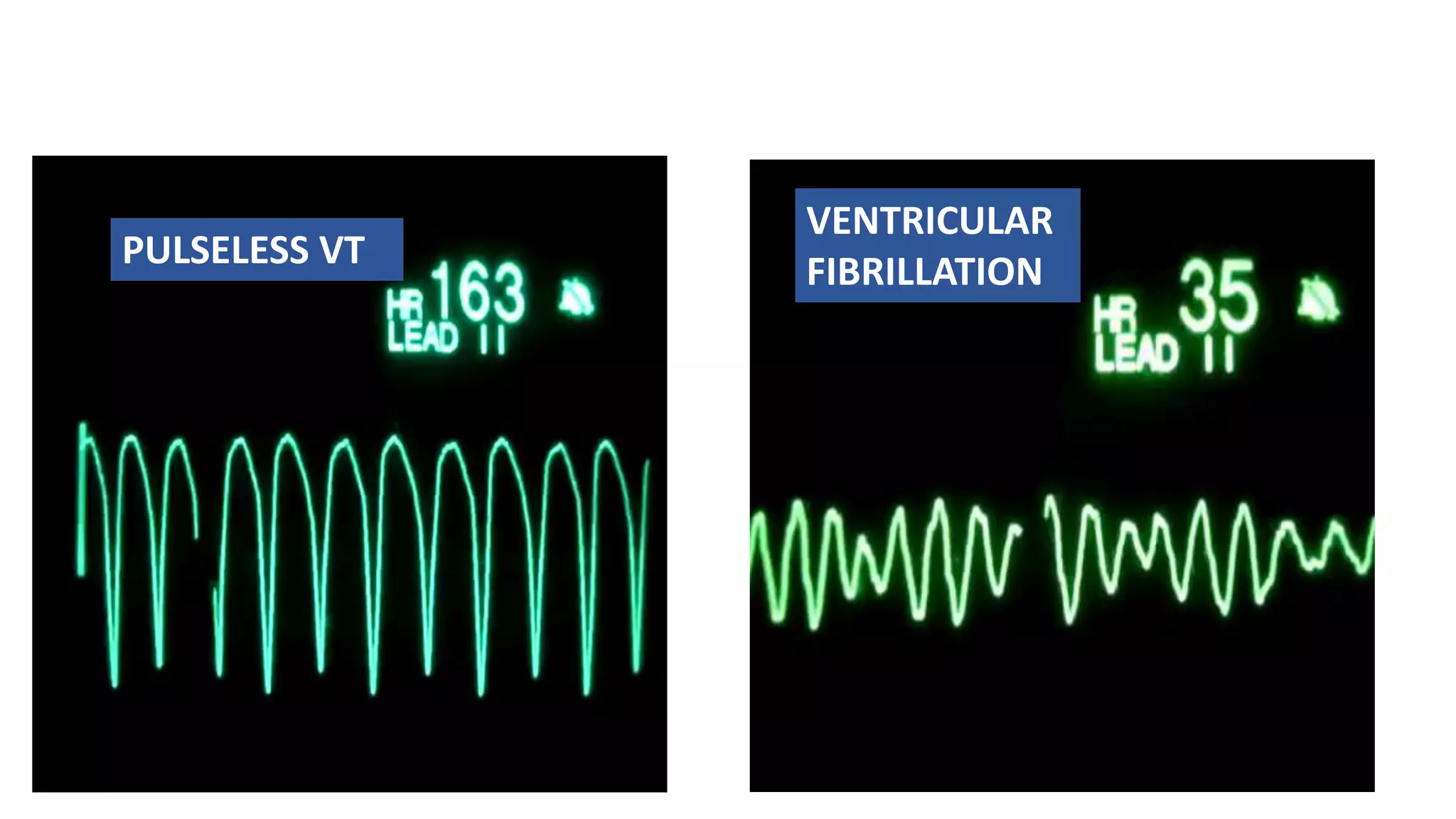
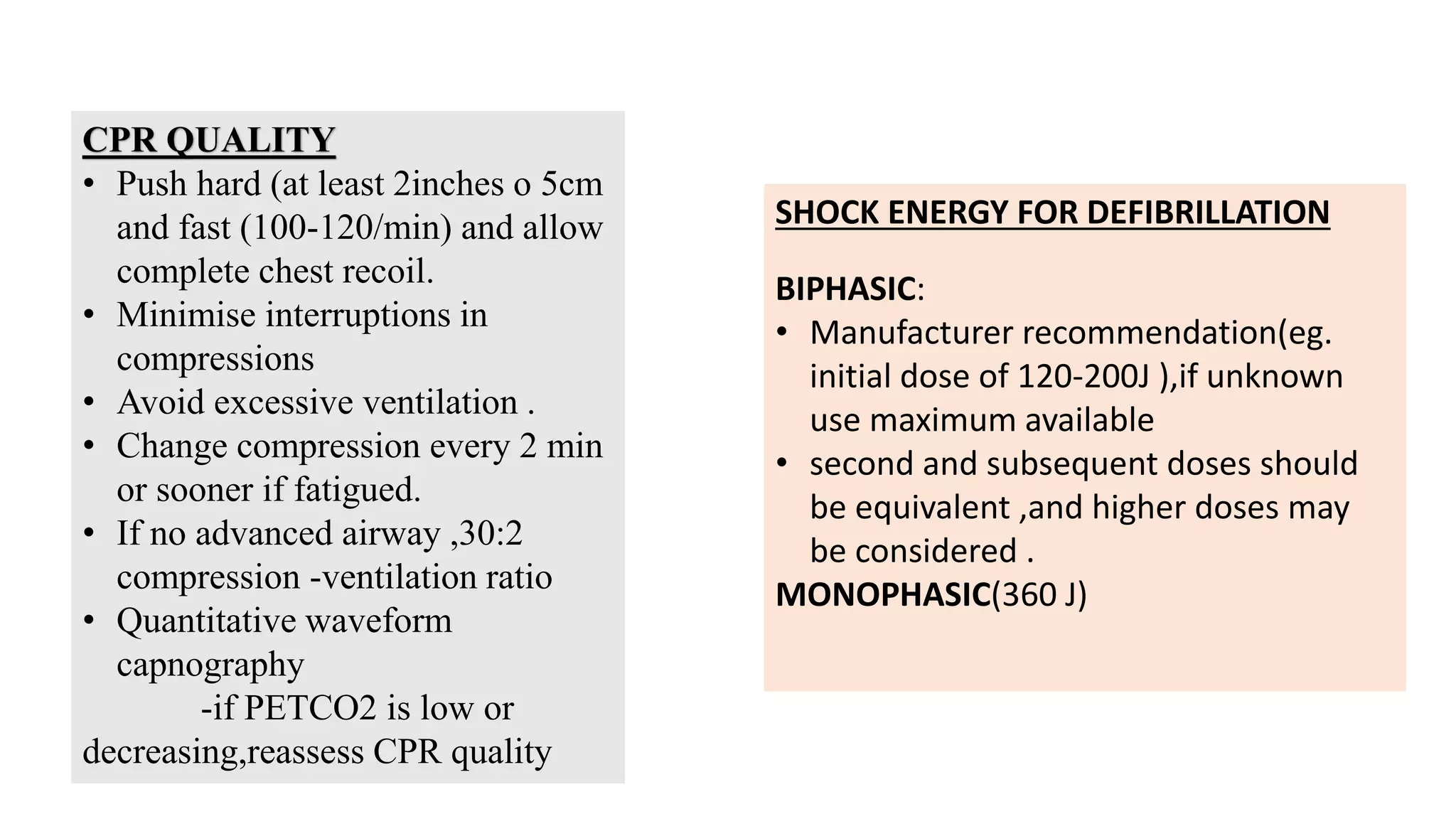
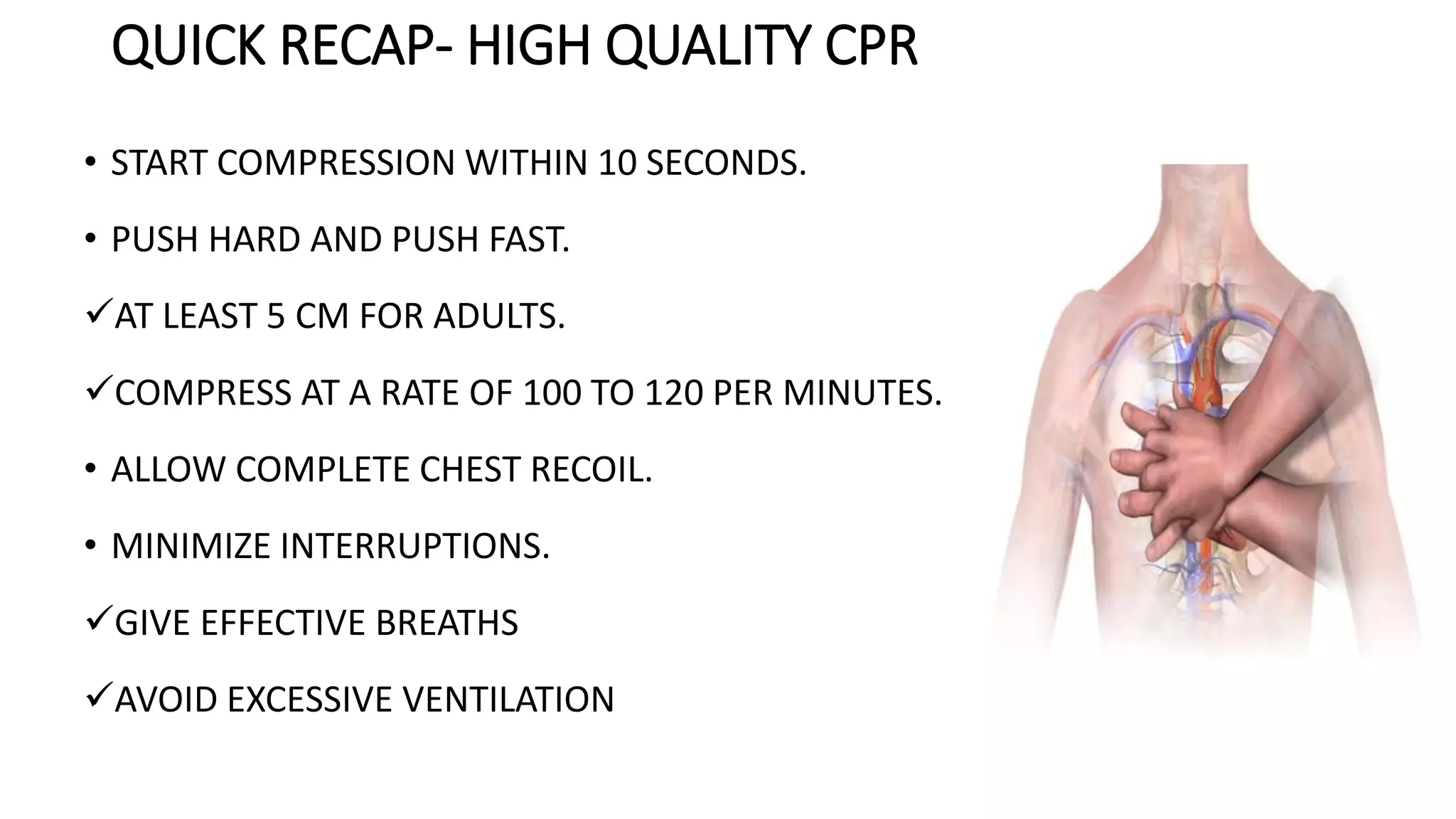
This document discusses adult basic life support (BLS) and advanced cardiac life support (ACLS). It outlines the steps of BLS, including high-quality chest compressions, airway management, use of an automated external defibrillator (AED), and importance of early CPR. It then describes the ACLS algorithm and management of cardiac arrest, including defibrillation, drug therapy like epinephrine and amiodarone, advanced airways, and treating reversible causes of cardiac arrest. The goal of BLS and ACLS is to restore spontaneous circulation through early recognition, high-quality CPR, defibrillation if needed, and treatment of underlying causes.