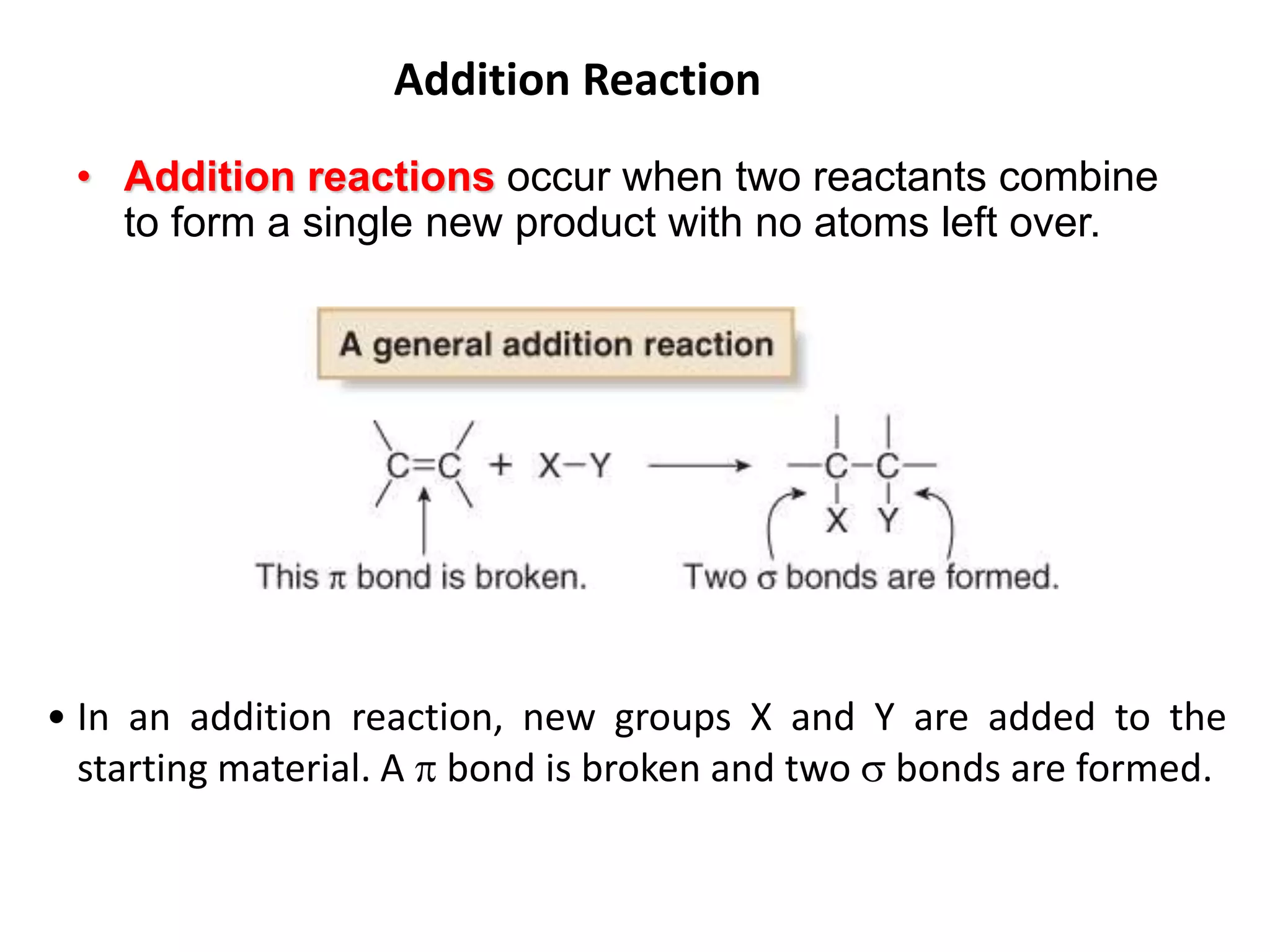
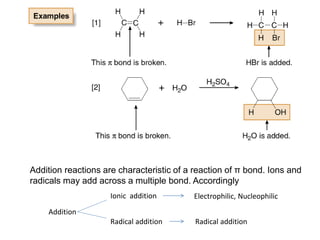
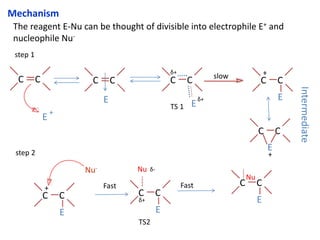
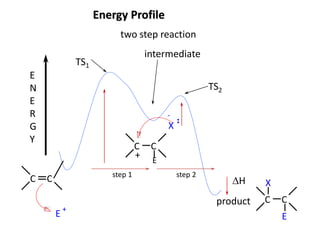
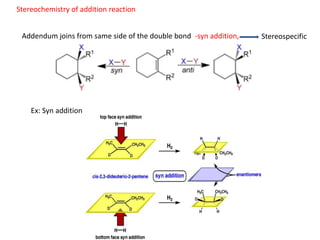
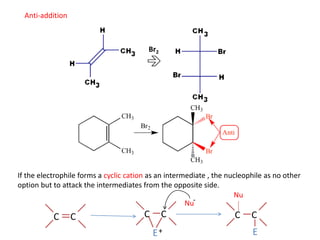
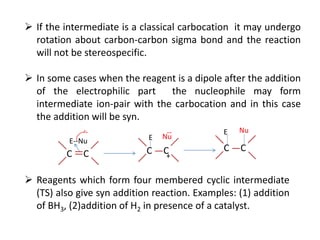
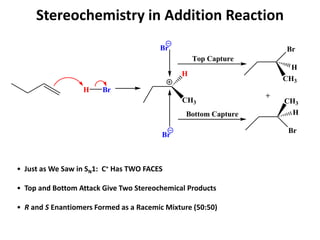
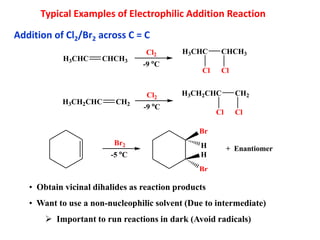
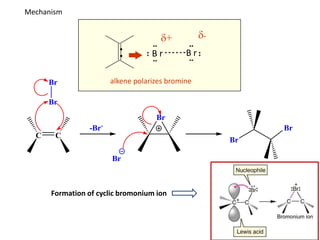
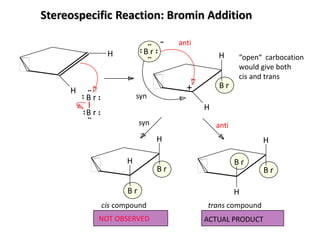
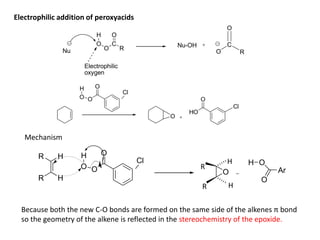
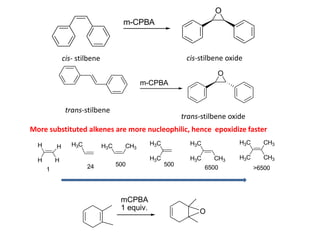
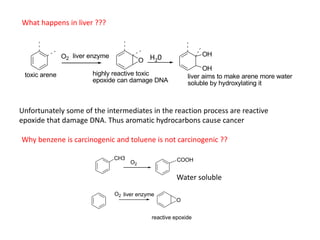
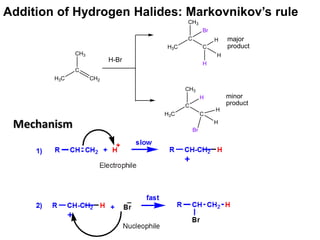
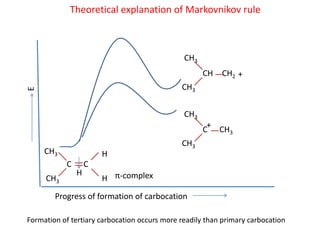
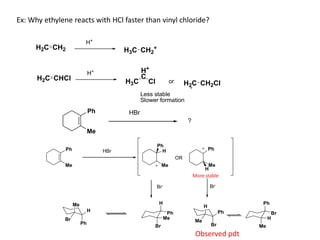
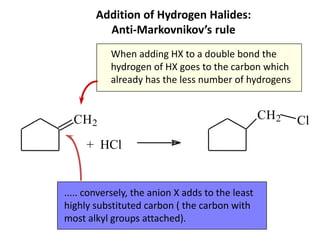
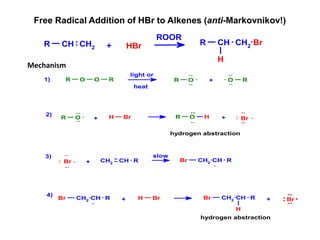
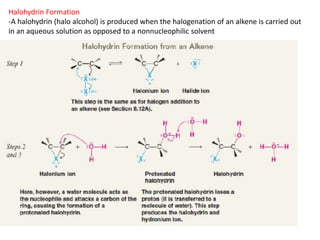
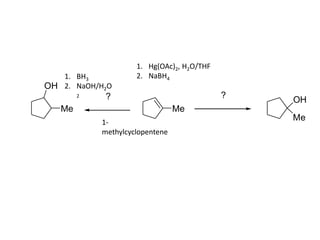
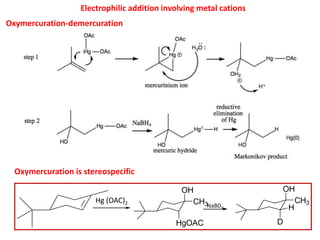
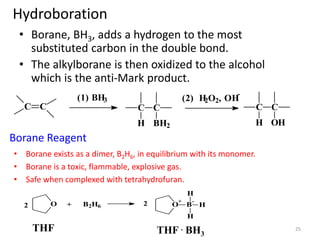
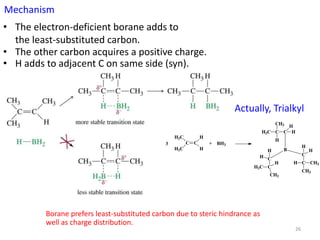
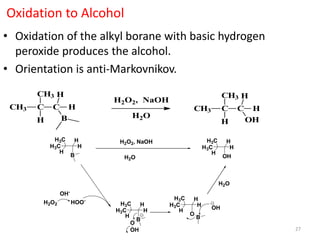
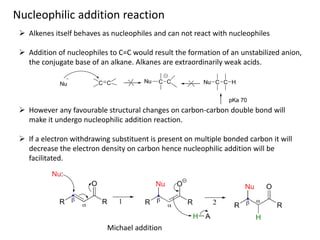
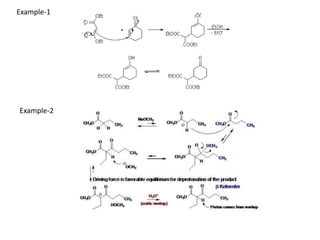
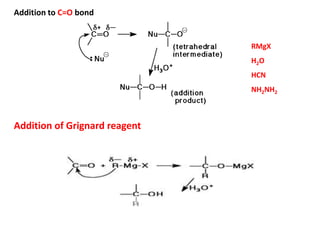
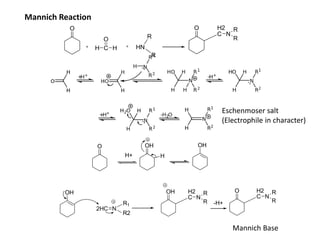
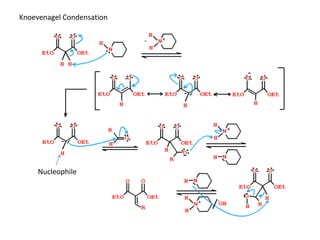
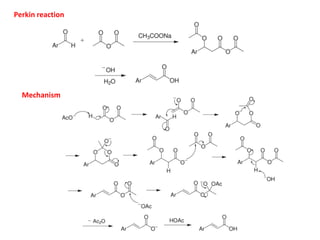
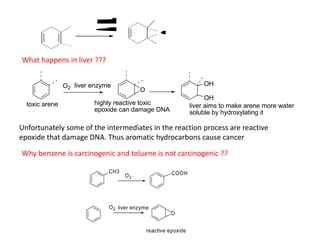
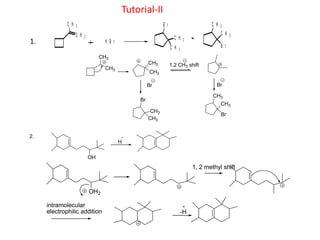
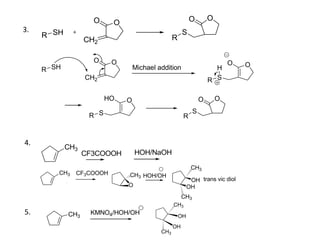
Addition reactions occur when two reactants combine to form a new product with no leftover atoms. In an addition reaction, new groups are added to the starting material, breaking a pi bond and forming two sigma bonds. Addition reactions involve the addition of electrophiles, radicals, or nucleophiles across multiple bonds such as carbon-carbon double or triple bonds.