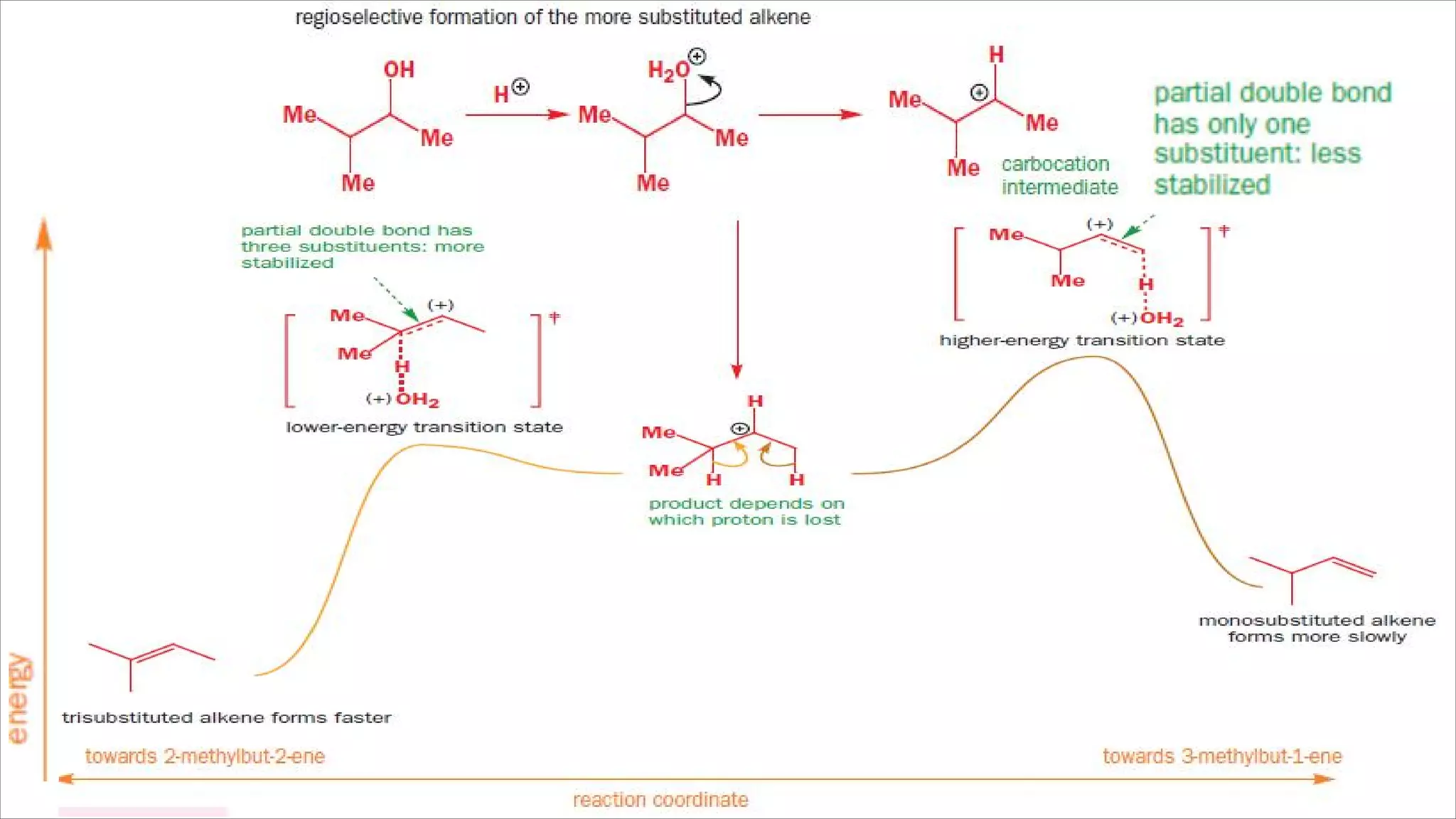
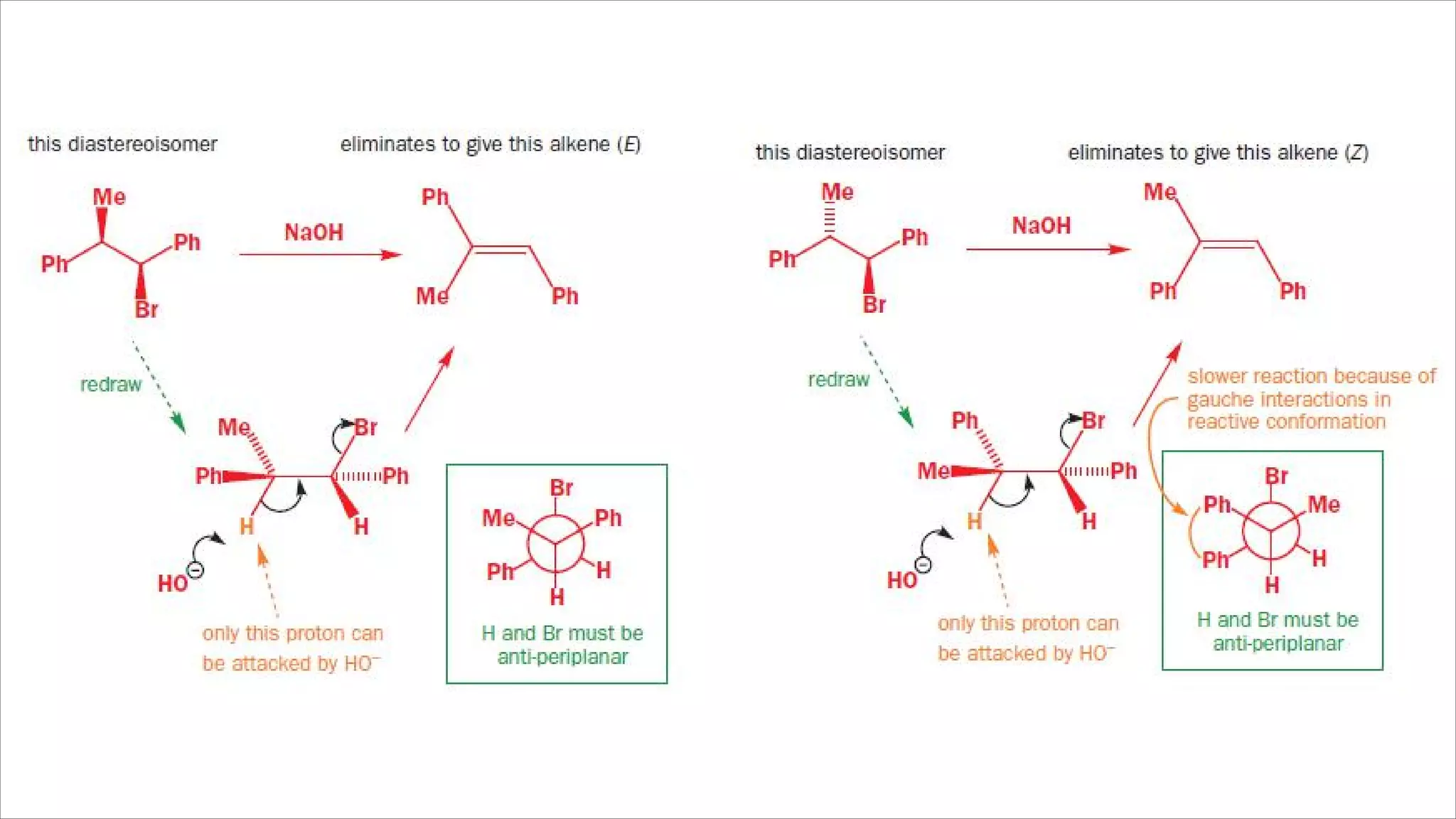
The document discusses stereoselective and regioselective E1 and E2 elimination reactions in organic chemistry, emphasizing how factors like sterics and substrate substitution affect the stability and formation of alkenes. It details how different conformations and orientations influence the product of the reactions, with examples such as tamoxifen highlighting the importance of stereochemistry in drug design. Additionally, it contrasts stereospecific reactions, which yield a single isomer, with stereoselective reactions, where one product is favored due to lower activation energy or greater stability.