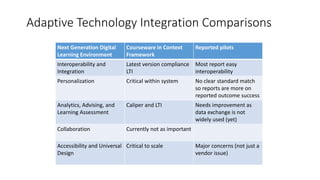
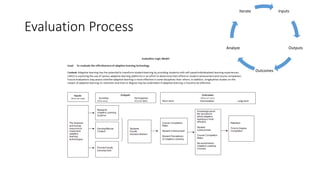
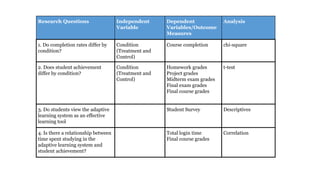
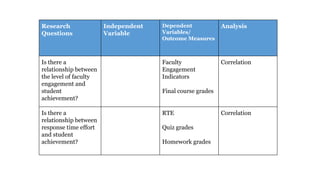
The document discusses adaptive courseware vendor selection and engagement for universities. It provides an agenda that covers introductions, vendor engagement, selection process, project management, setting expectations, changing culture, iterating and scaling pilots. It describes the author's background and experience. It outlines the selection process universities can use, including looking at efficacy research. It also discusses what information and frameworks were lacking for universities prior to conducting pilots. The rest of the document provides details on the vendor selection, project management, challenges encountered, lessons learned, and changing university culture to support innovation.