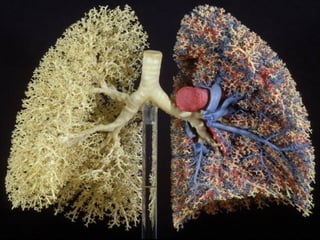
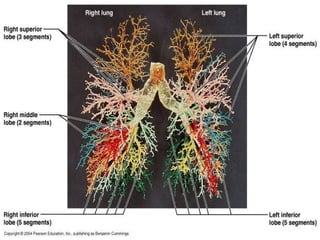
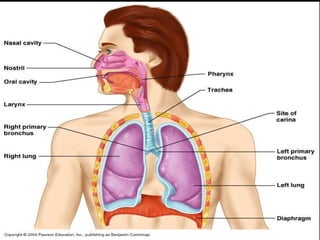
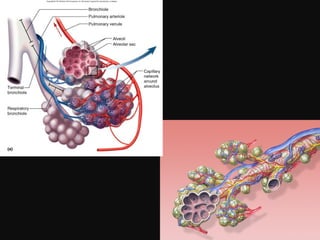
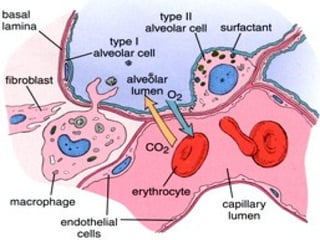
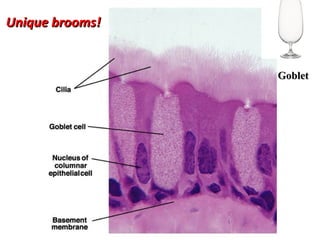
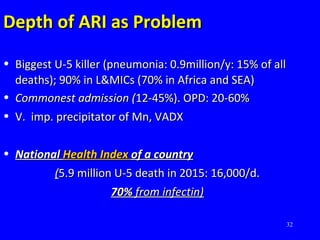
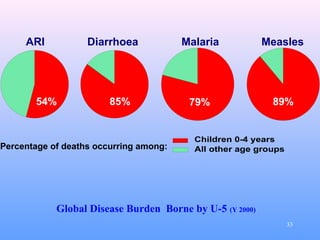
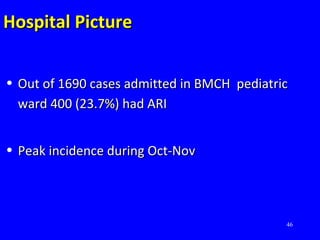
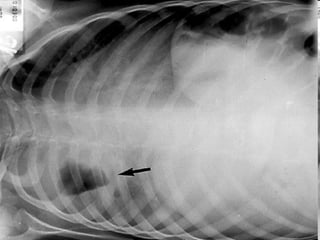
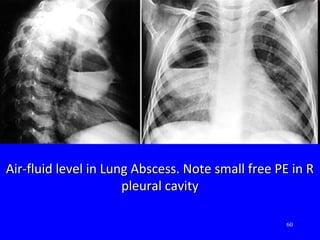
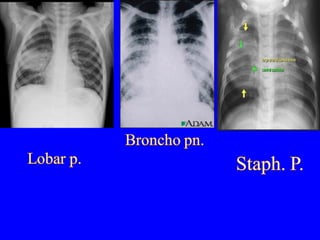
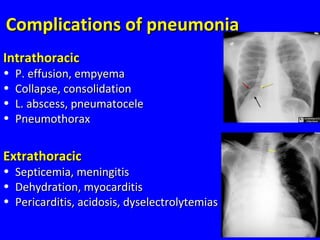
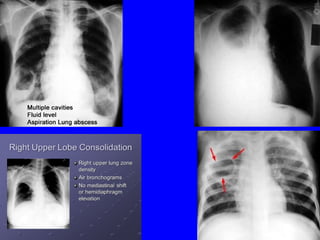
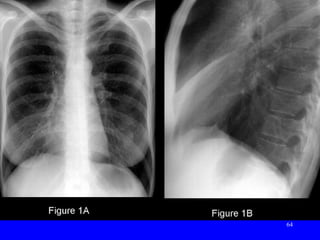
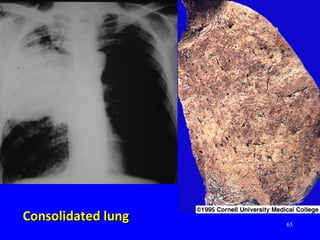
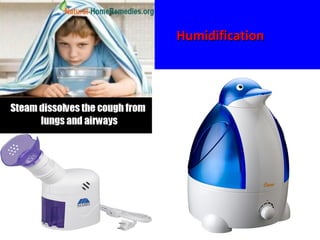
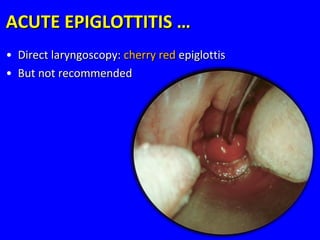
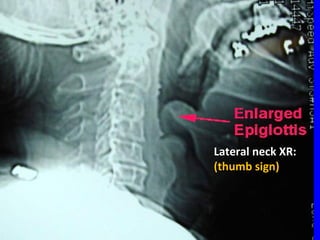
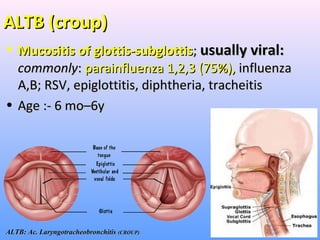
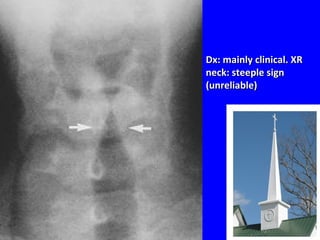
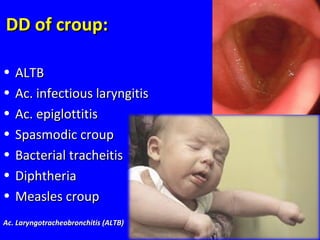
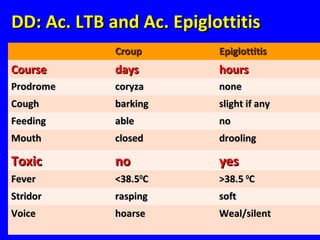
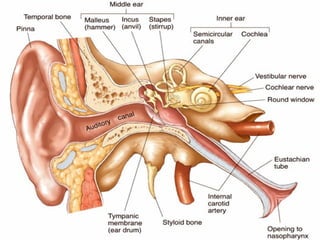
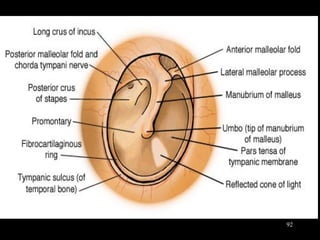
- Acute respiratory infections (ARIs) are a major cause of death in children under 5 years old, especially in low and middle income countries. Pneumonia alone causes 15% of under-5 deaths globally.
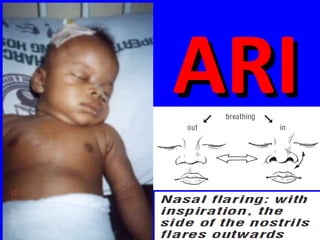
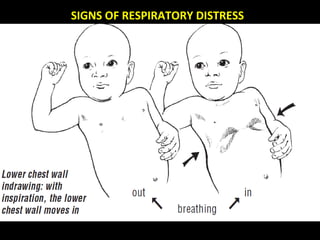
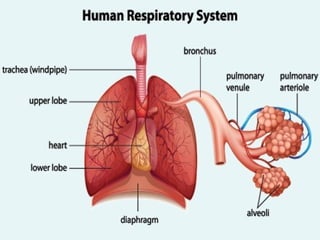
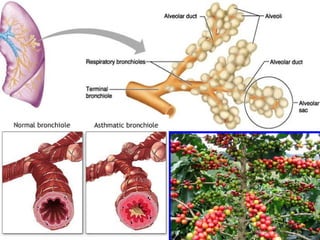
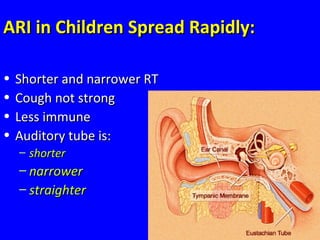
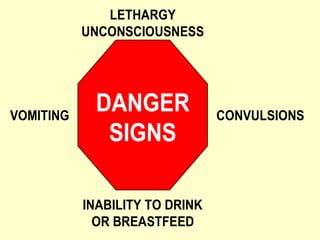
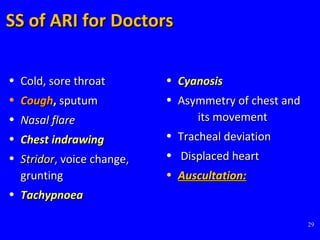
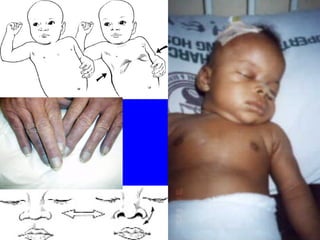
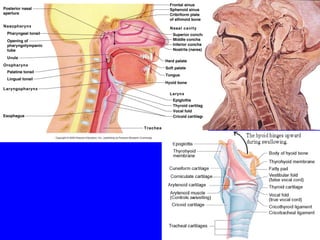
- ARIs spread rapidly in children due to their shorter, narrower respiratory tracts and weaker cough. Signs include fast breathing, chest indrawing, and general danger signs. ARIs can lead to malnutrition, vitamin A deficiency, and other issues.
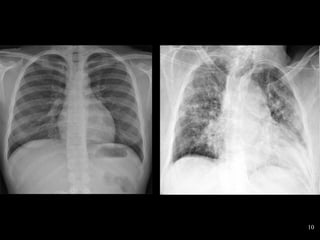
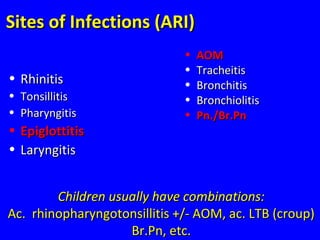
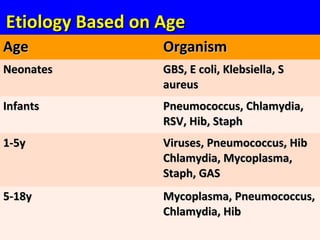
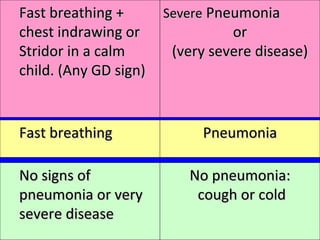
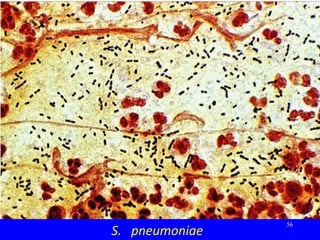
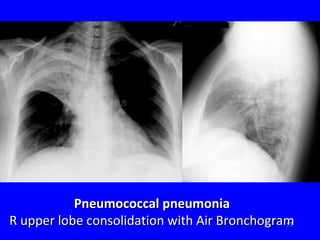
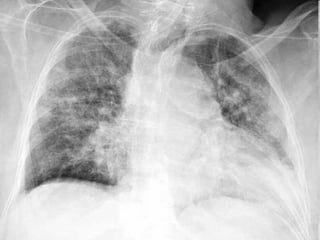
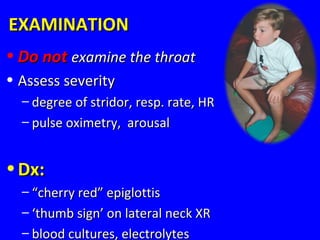
- ARIs have various causes including viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Treatment focuses on classifying pneumonia severity based on Integrated Management of Childhood Illness guidelines and providing appropriate low-cost antibiotics. While a major problem, deaths from AR