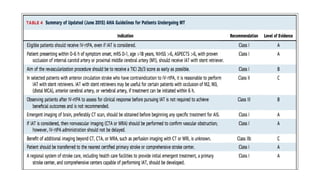
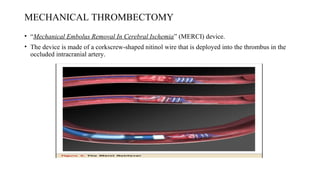
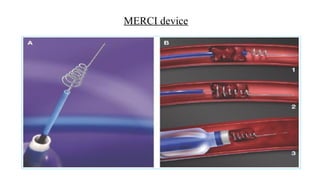
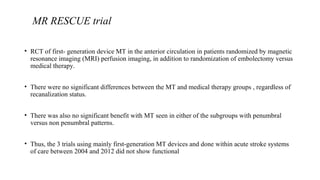
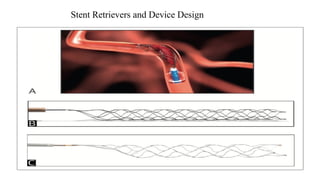
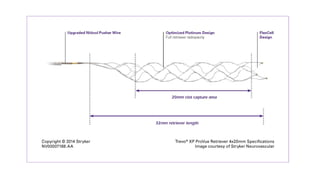
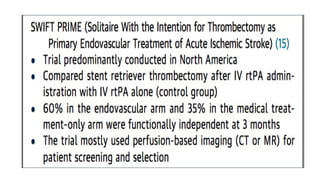
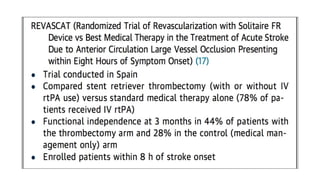
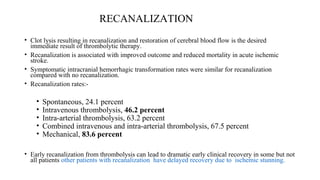
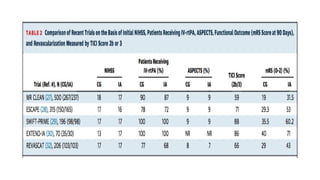
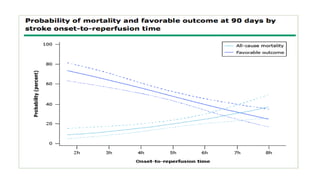
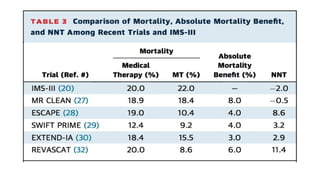
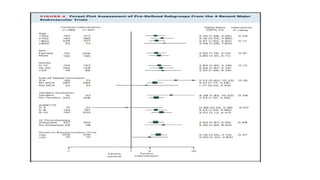
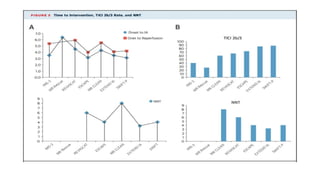
The document discusses the evolution of treatments for acute ischemic stroke (AIS), including intravenous thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy. It summarizes key randomized trials that established the benefits of mechanical thrombectomy. The first-generation trials using early thrombectomy devices did not show benefit, but recent trials using stent retrievers demonstrated significantly improved recanalization rates and superior outcomes for mechanical thrombectomy combined with intravenous thrombolysis compared to intravenous thrombolysis alone in eligible patients presenting within 6 hours of stroke onset. The document concludes that mechanical thrombectomy is now a standard treatment for AIS but remains underutilized.







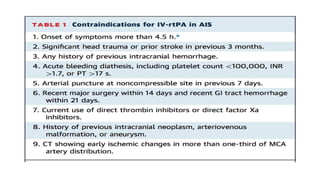































![Exclusion criteria
1. Arterial blood pressure >185/110 mmHg
2. Blood glucose <2.7 or >22.2 mmol/L
3. Intravenous treatment with thrombolytic therapy in a dose exceeding 0.9 mg/kg
alteplase or 90 mg
4. Laboratory evidence of coagulation abnormalities (eg, platelet count <40,000/mL [40 x
109/L] or International Normalized Ratio [INR] >3.0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strokeinterventions-161103153913/85/acute-ischemic-Stroke-interventions-59-320.jpg)