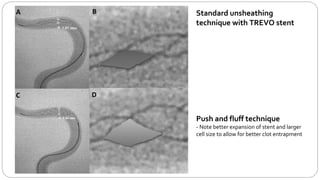
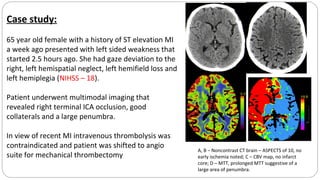
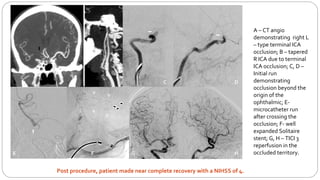
This document describes the push and puff technique for mechanical thrombectomy and one physician's experience using this technique with the Solitaire stent retriever. It summarizes a case study of a 65-year-old female patient who presented with left-sided weakness and was found to have a right terminal ICA occlusion that was successfully treated with mechanical thrombectomy using the push and puff technique. The physician's early experience using this technique with the Solitaire device in 7 patients demonstrated a 100% first pass reperfusion rate and modified TICI 3 reperfusion in 85% of patients. Commonly encountered challenges after stent retrieval included vessel spasm and residual thrombus. The conclusion is that the push and puff technique appears very promising for improving outcomes