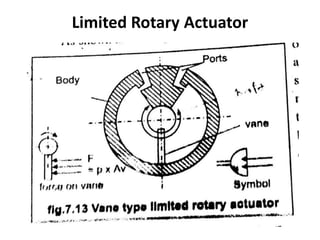
The document classifies hydraulic actuators into linear and rotary types, detailing various cylinder constructions like single acting, double acting, and their special forms. It discusses design considerations for hydraulic cylinders, such as required thrust, speed, and service life, and also reviews hydraulic motors including their advantages like compactness and high power-to-weight ratio. Additionally, it mentions limitations of gear motors and other rotary actuator types.