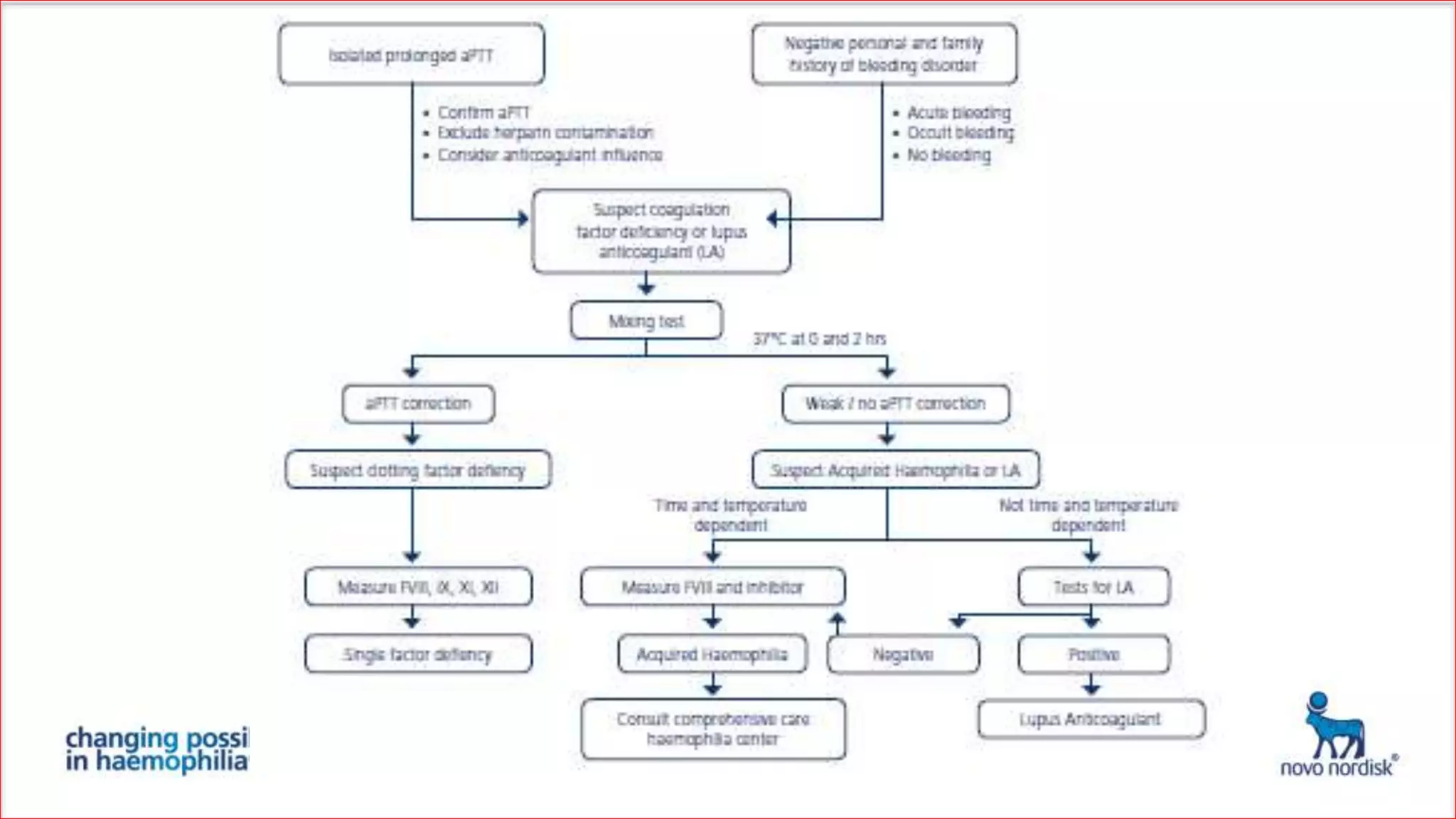
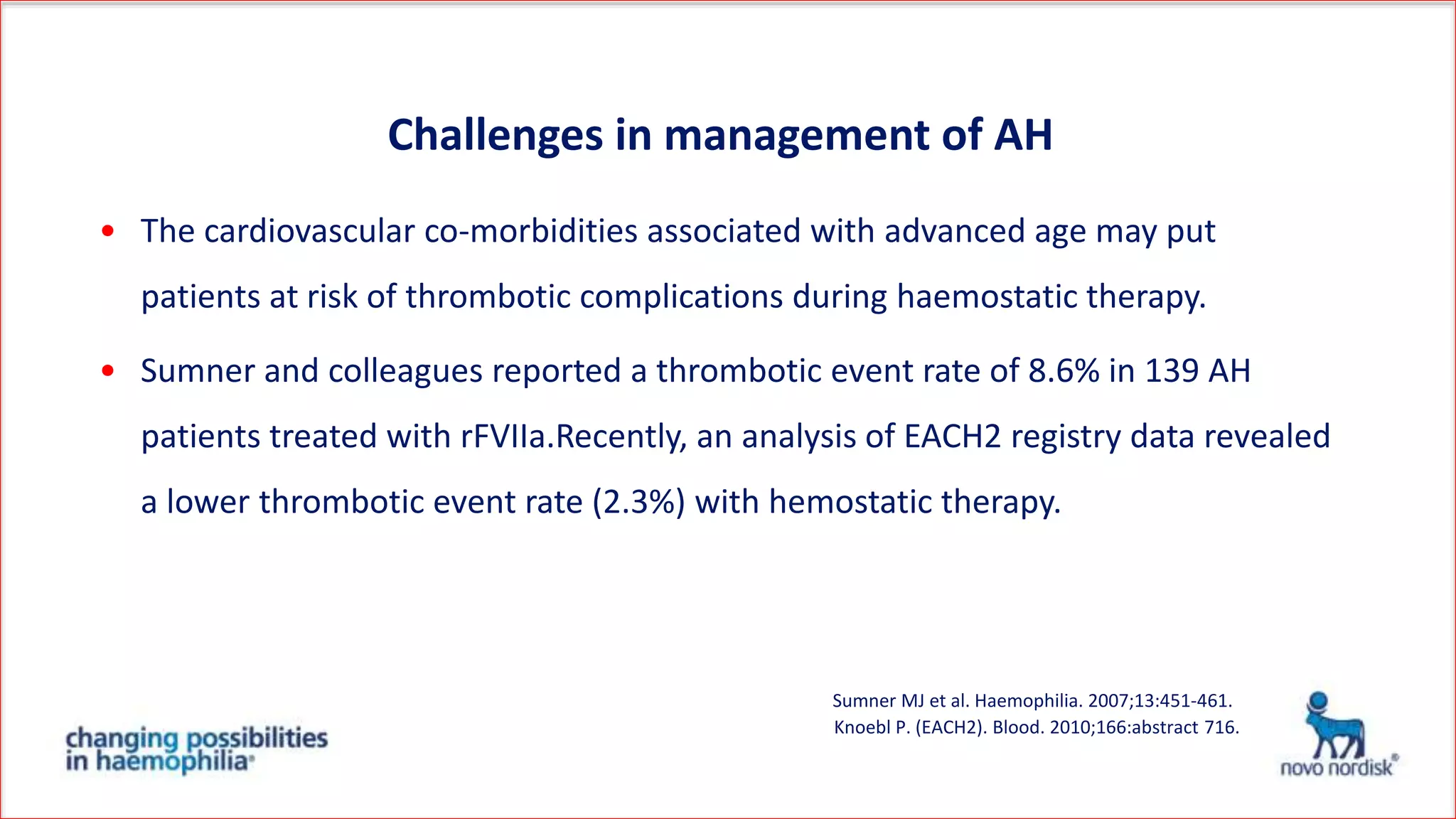
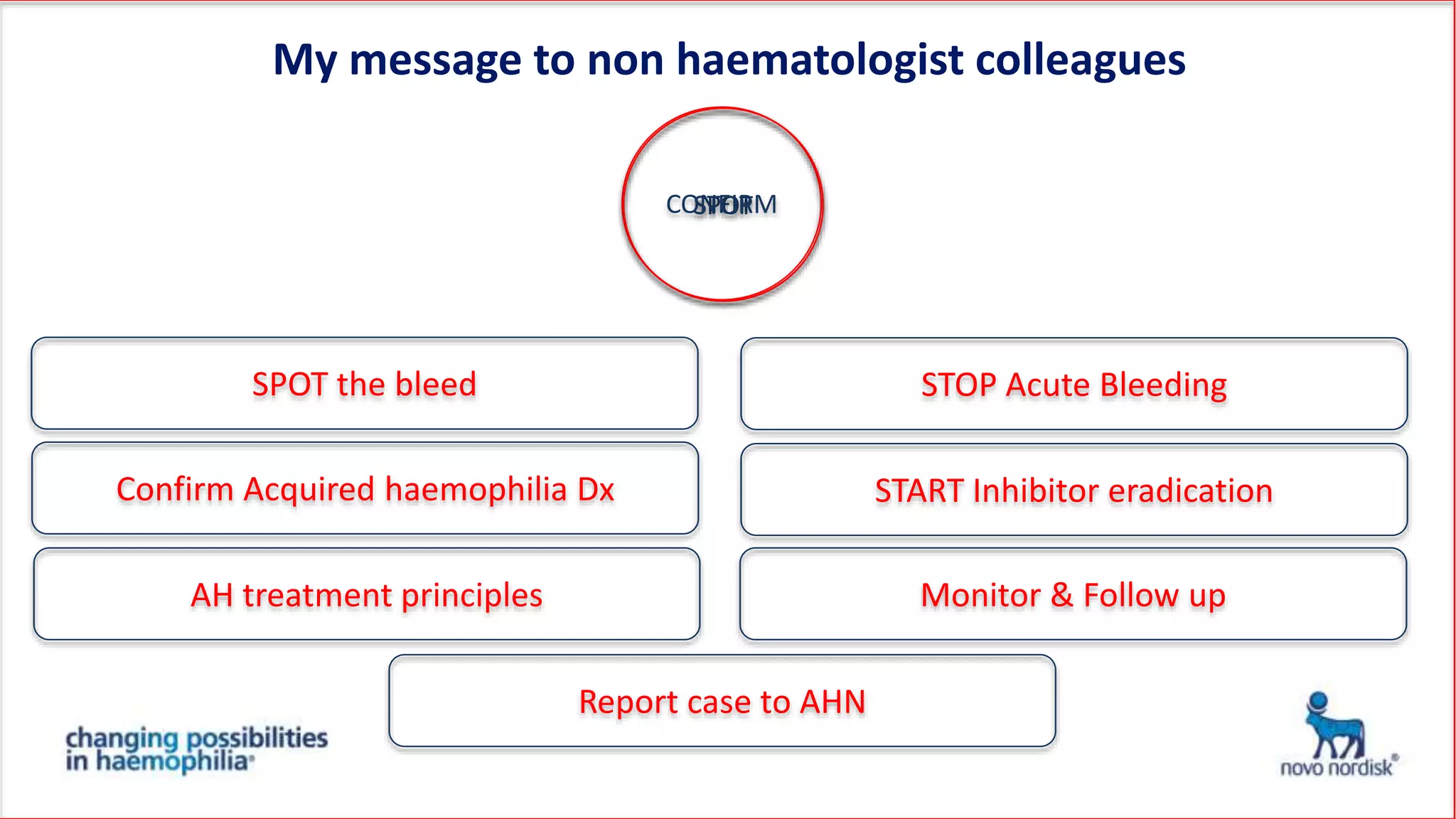
The document discusses acquired haemophilia from the perspective of non-haematologists, detailing two case studies involving patients with this rare bleeding disorder. It highlights the challenges in diagnosing and managing acquired haemophilia, emphasizing the need for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment strategies to control bleeding and eliminate inhibitors. Awareness and collaboration among various medical specialties are essential to improve outcomes and reduce morbidity and mortality associated with the condition.