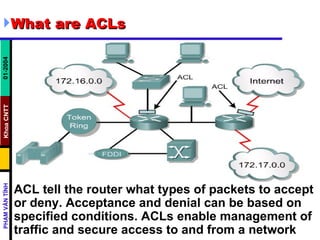
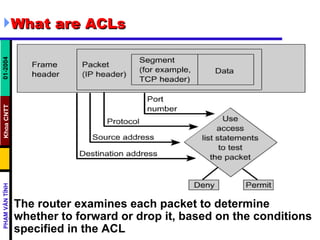
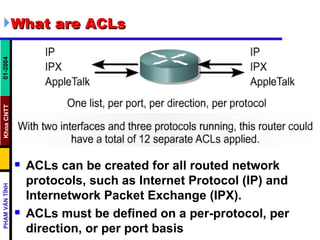
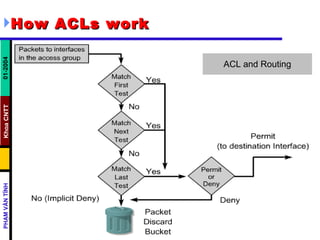
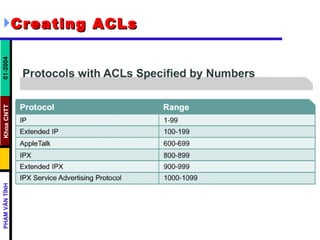
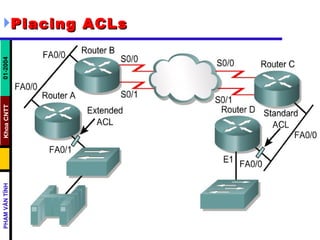
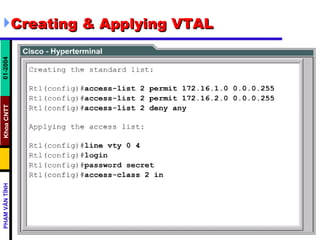
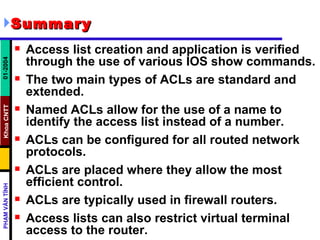
ACLs control and manage network traffic by allowing or denying packet access based on conditions. Standard ACLs are used to filter traffic by source IP address only, while extended ACLs filter by source/destination IP address, protocols, and ports. ACLs are created with permit or deny statements and applied to interfaces using access lists or to virtual terminal lines using access classes to restrict access. Wildcard masks are used to filter groups of IP addresses in an access list.