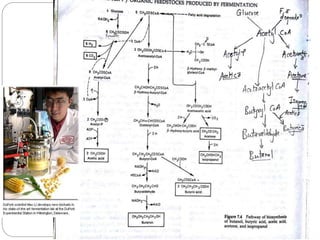
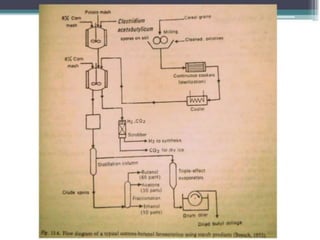
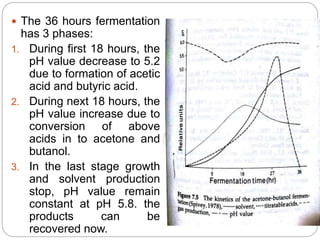
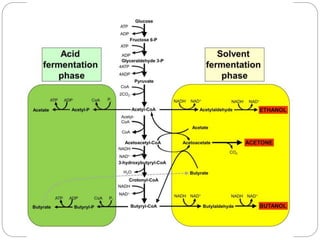
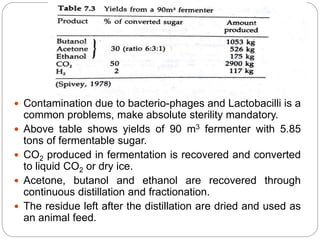
The document summarizes the acetone-butanol fermentation process. It notes that Clostridium acetobutylicum bacteria are used to produce acetone and butanol through fermentation of sugars from sources like molasses. Historically, this fermentation was important for producing explosives and synthetic rubber. Modern plants were replaced by petroleum processes after World War II, though some still operate. The process involves three phase fermentation at 34°C over 36 hours to produce solvents, which are then recovered through distillation. Products like butanol and acetone have various industrial uses.