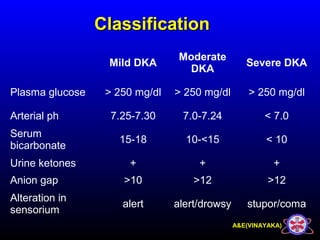
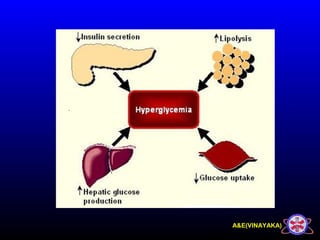
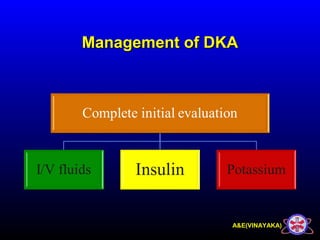
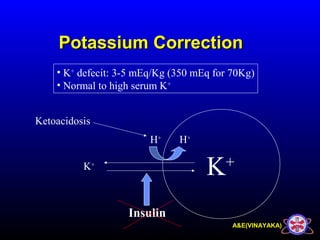
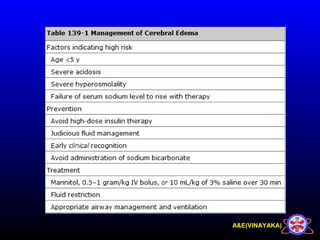
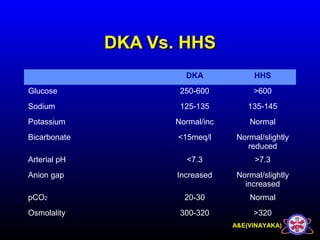
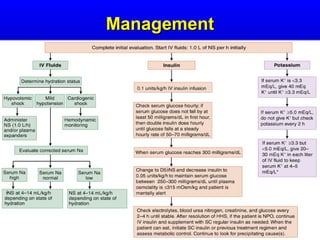
This document discusses diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), providing information on its pathophysiology, classification, precipitating factors, signs and symptoms, laboratory investigations, management, and goals of treatment. It classifies DKA as mild, moderate or severe based on plasma glucose, arterial pH, serum bicarbonate, urine ketones, and anion gap. The key aspects of management include fluid resuscitation to restore intravascular volume, insulin therapy to reduce glucose and ketone levels, and potassium supplementation to correct deficiencies. Bicarbonate supplementation is only recommended if the pH is less than 6.9.