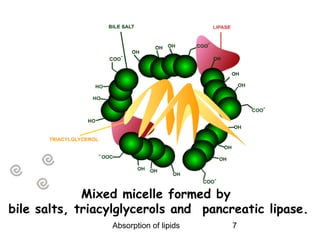
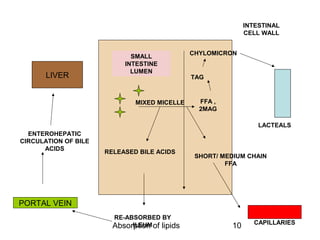
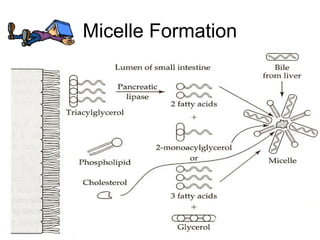
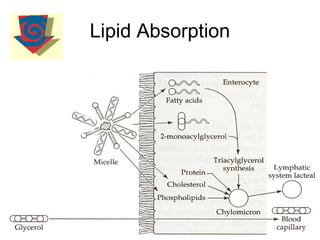
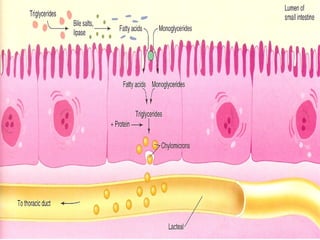
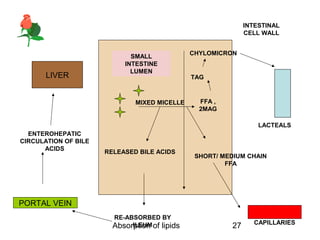
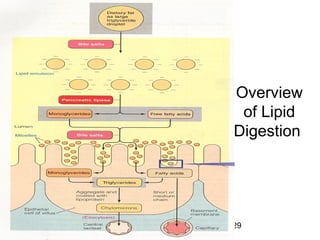
1) Lipids undergo digestion into monoglycerides, fatty acids, cholesterol, and phospholipids. These products associate with bile salts to form mixed micelles that transport the lipids across the intestinal cells.
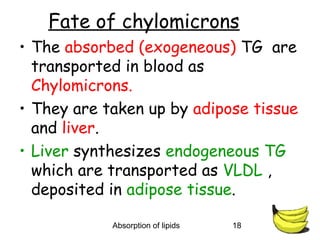
2) Inside the intestinal cells, the lipids are reformed into triglycerides and assembled into chylomicrons along with proteins. Chylomicrons enter the lymphatic system and eventually the blood.
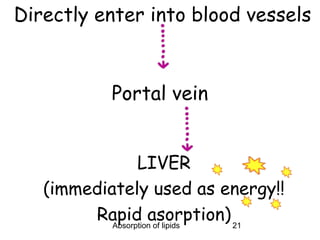
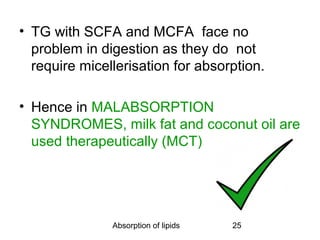
3) Short and medium chain fatty acids do not require micelle formation or re-esterification and enter the blood directly to be used for energy or transported to the liver. Long chain fatty acids in chylomicrons are taken up by tissues for storage or used for energy.