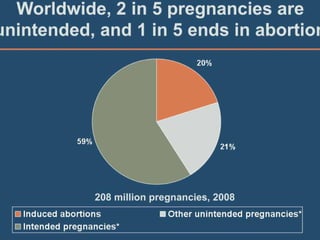
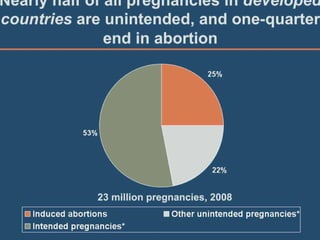
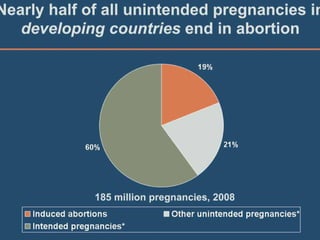
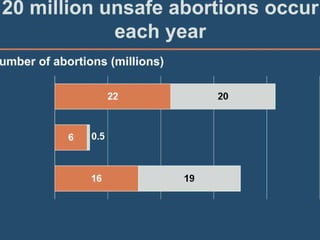
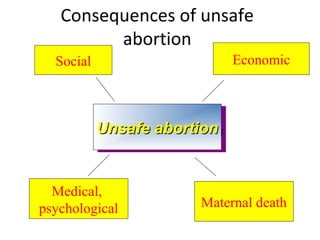
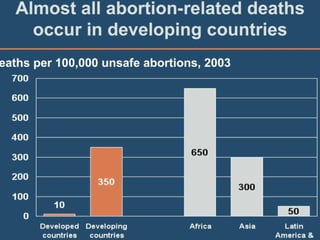
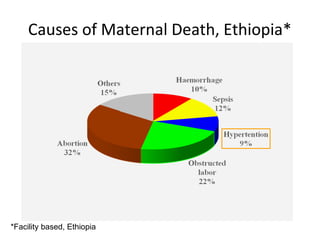
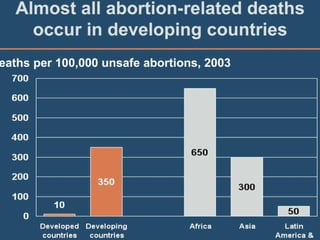
This document discusses abortion and post-abortion care. It defines abortion and classifies the different types. It also discusses the magnitude of abortion globally and in Africa and Ethiopia. It then covers spontaneous abortion, including risk factors and potential causes. It discusses the clinical features and diagnosis of abortion. It defines post-abortion care and its five key elements. It notes that unsafe abortion is a major cause of maternal mortality worldwide and in East Africa.