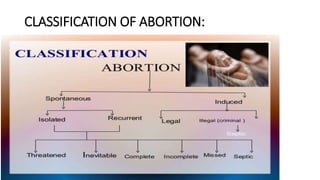
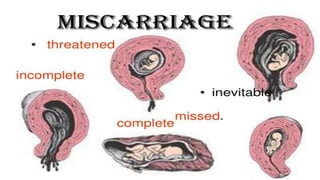
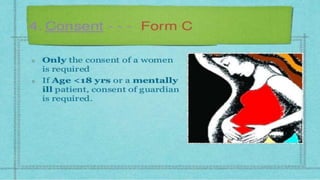
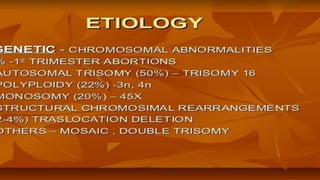
This document discusses various types of abortion including spontaneous, threatened, inevitable, incomplete, complete, missed, recurrent, septic, induced, and illegal abortions. It defines each type, describes their signs and symptoms, and outlines recommended management and treatment approaches. Complications of abortion are also reviewed along with methods for termination of pregnancy in the first and second trimesters.